How to manage DO in Activated sludge plants?
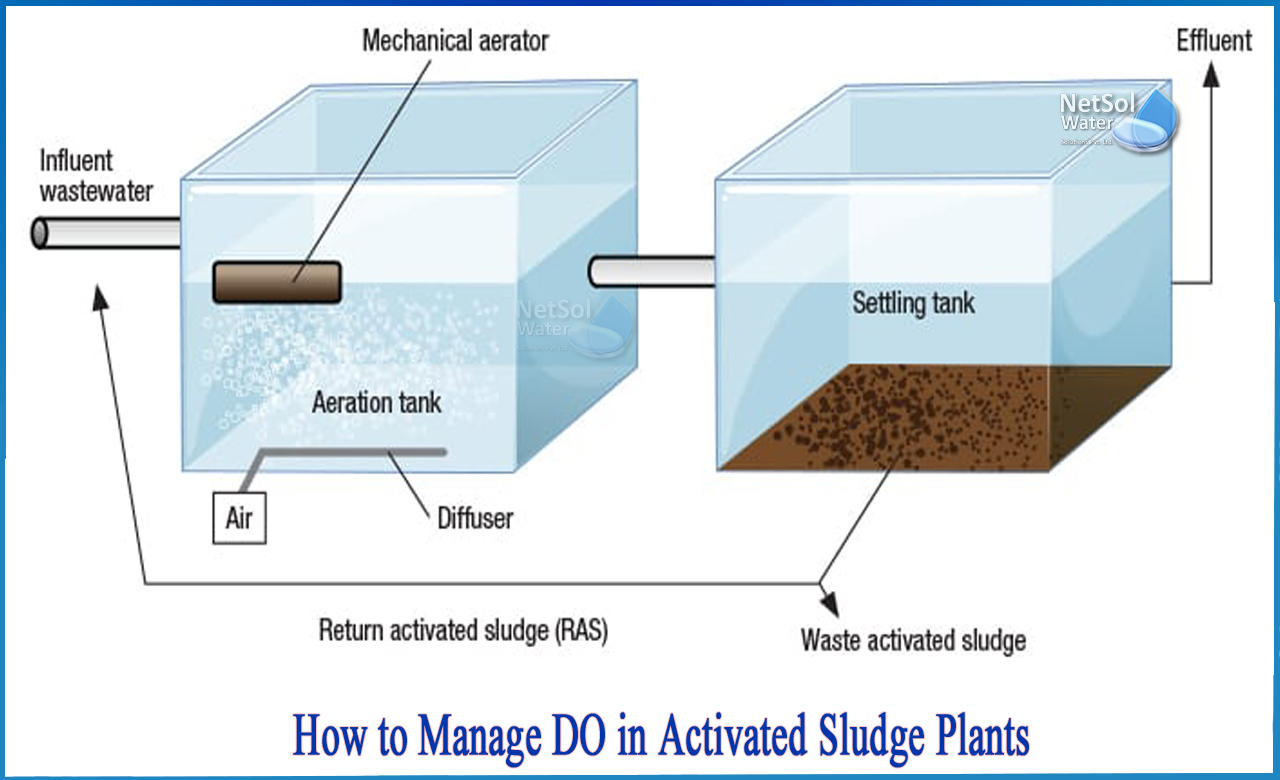
The activated sludge method is a wastewater treatment process that employs aeration and a biological floc made up of bacteria and protozoa to treat sewage or industrial wastewater. The overall structure of an activated sludge process for removing carbonaceous pollutants includes the following items:
In an aeration tank, air (or oxygen) is pumped into the mixed liquor. The biological flocs (the sludge blanket) are then allowed to settle in a settling tank (sometimes known as a "final clarifier" or "secondary settling tank"), separating the biological sludge from the clean treated water.
Why should we maintain DO in ASP’s?
Maintaining adequate dissolved oxygen levels in activated sludge facilities is critical for the biological treatment of organic matter and ammonia. While raw wastewater frequently includes some oxygen, aeration systems can improve dissolved oxygen (DO), mixing, and microbial suspension by mechanical agitation or diffused aeration. This oxygen is used by aerobic bacteria to degrade organic waste into inorganic byproducts.
Biochemical oxygen demand is the quantity of dissolved oxygen used by bacteria during biological therapy (BOD). When one pound of ammonia is oxidised, that value rises to 4.57 pounds of oxygen. Most plants strive to keep DO levels around 2 mg/L, which permits bacteria in the floc's core to get oxygen.
Wastewater operators should assess oxygen availability in the form of dissolved oxygen on a frequent basis. Aerobic and nitrifying bacteria will die as oxygen levels fall, and floc will break apart. The possibility for filamentous development rises when DO concentrations fall below 1 mg/L. On the opposite end of the spectrum, too much oxygen increases power consumption and, at extremely high levels, prevents settling.
According to research, aeration can account for up to 45 to 75 percent of a treatment facility's total power use. According to the findings, energy expenses may be decreased by up to 50% when using an online DO analyser with automatic controls.
Operators can accurately assess if DO concentrations are sufficient for treatment while creating a DO profile by taking repeated samples in the same place throughout the week. Furthermore, monitoring DO at various depths and places in the aeration tank can aid in the detection of dead patches.
It is worth noting that temperature, pressure, and salinity may all have an effect on oxygen solubility. Raw wastewater, aerobic/anaerobic digester, and final effluent can all be sampled in addition. High dissolved oxygen in final effluent can induce eutrophication in receiving waterways, whereas low DO can damage aquatic life. Some licences require a minimum DO level for effluent to guarantee that aquatic species have enough oxygen to survive.
In wastewater treatment systems, dissolved oxygen is a commonly measured metric. Operators must understand how dissolved oxygen (DO) is involved in wastewater operations and how to regulate DO to achieve compliance.
Analytical instruments:
Traditional methods for monitoring pollution levels in water and wastewater are laboratory-based equipment that measure the oxygen demand required to oxidise contaminants. The standard instruments are Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) and Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD). The oxygen-depleting effects of waste pollutants are calculated using BOD and COD. The measurement of Total Organic Carbon (TOC), which directly detects inorganic and organic carbon, is an exception to this rule.
BOD or BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMANDis a measure of the proportion of organic matter that bacteria may breakdown and is generally expressed as the amount of oxygen utilised (mg/L) during five days at 20°C. BOD comprises organic carbon that degrades fast (carbonaceous or cBOD) and, on rare cases, ammonia (nitrogenous or nBOD). Organic carbon molecules that are soluble, particulate, or colloidal are the primary source of BOD (cBOD).
COD or CHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMANDis the amount of oxygen required for the chemical oxidation of compounds in water. This need is determined utilizing a strong oxidant, most often dichromate and, to a lesser extent, permanganate.
For more details, contact Netsol Water.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.