WHAT IS GROUND WATER?
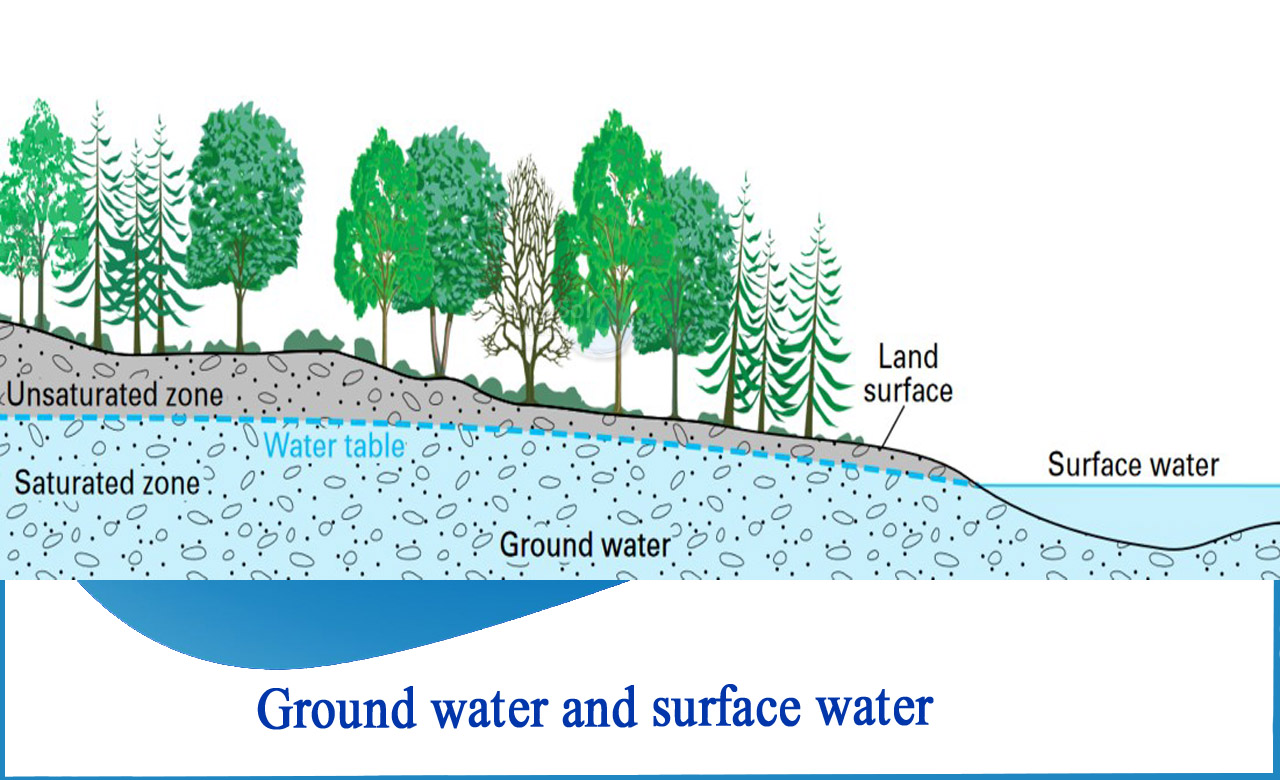
Groundwater is the water that exists beneath the Earth's surface in the pore spaces of rocks and soils, as well as in the fractures of rock formations. When a unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit supplies useable amount of water, it is called an aquifer. The water table is the depth at which soil pores, cracks, and cavities in rocks become totally saturated with water. Groundwater is refilled from the surface, and it can naturally release at springs and seeps, forming oasis or wetlands. Extraction wells are frequently built and operated to extract groundwater for agricultural, municipal, and industrial purposes.
WHAT IS SURFACE WATER?
The nation's surface-water resources, the water in its rivers, streams, creeks, lakes, and reservoirs are critical to our daily lives. Surface water is mostly used for drinking water and other public purposes, irrigation, and cooling of electricity-generating equipment in the thermoelectric power industry.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN GROUND WATER AND SURFACE WATER
The fundamental distinction between groundwater and surface water is their respective water quality. Surface water can have significant levels of toxins as a result of air fallout and runoff, necessitating considerable treatment before it can be used as a community's water source. Chemical contaminants that collect as a result of runoff are frequent in surface water.
Despite the fact that groundwater is usually cleaner than surface water, it can nevertheless include a variety of toxins. Seepage and soil percolation are the sources of these pollutants. The sediment layers located below the water table, on the other hand, can naturally filter the water to eliminate at least some of the toxins. Because groundwater contains fewer impurities, it requires less treatment before being utilised as drinking water.
Even though groundwater is the primary source of drinking water across the country, it's crucial to remember that only some groundwater is easily accessible. Groundwater makes up over 98 percent of all freshwater on the planet.
Another reason groundwater is frequently preferred over surface water is that it is more available during droughts. When a drought strikes, most surface water evaporates, posing a problem for industries that rely on surface water as their principal source of water. Groundwater is less expensive and easier to clean than surface water since it contains less impurities. While surface waters can be found in streams and lakes, groundwater can be reached through wells wherever it is needed, making it more accessible.
Although groundwater is mostly utilized to replenish drinking water sources, it can also be used for a variety of other purposes. Geothermal energy can be used to construct very energy-efficient HVAC systems by tapping into groundwater. A number of major facilities have begun to use groundwater for heating and cooling their structures.
MINERALS IN GROUND WATER
Water dissolving the substances it comes into touch with is a typical source of contamination in groundwater. Water, in fact, dissolves more compounds directly than any other liquid. Hard water is a term used to describe water that has a lot of minerals in it. Hard water contains a high concentration of ions such as magnesium and calcium. Soft water, on the other hand, has a low or non-existent mineral content.
Magnesium and calcium concentrations will be determined before being converted to calcium carbonate to determine the hardness of water.Water hardness is an important metric in many businesses since it shows how clean the water is. Many of the systems and components used in an industrial setting can be severely harmed by hard water.
While both groundwater and surface water can be used for a variety of purposes, groundwater is more readily available in practically every part of the country, making it easier to acquire. Despite the decreased concentration of toxins in groundwater, it's critical to test and treat any groundwater you use before using it.