What are membranes?
Membranes are barriers in water treatment that allow water to pass through while preventing unwanted substances from passing through as well. Technical membranes filter salts, impurities, viruses, and other particles from water in the same way that cell walls do in our bodies.
What is a membrane process in Waste Water Treatment?
A membrane process is any method that filters or removes particles from water by using a membrane barrier. The pressure difference between one side of the membrane and the other causes fluids to pass through the membrane. Contaminants cling to one side. Although many different types of filtering media are used for water treatment, such as clay, silt, and sand, one property that distinguishes membranes is their ability to separate smaller substances from a liquid, such as salts and ions.
Membrane processes are physical particle diffusion processes in water. They work because certain types of membranes allow particles with specific characteristics to pass through while blocking particles with different characteristics from passing through.
With the development of high-performance synthetic membranes in the 1960s, membranes emerged as a viable method of water purification. Membranes for water treatment have advanced in their use, with more advanced membranes made from new materials and used in a variety of configurations. The scarcity of fresh water sources has fueled a push for alternative resources such as ocean water.
Why are membranes used?
Membranes are increasingly being used to produce potable drinking water from ground, surface, and seawater sources, as well as for advanced wastewater treatment and desalination. Over the last two decades, these technologies have been among the most widely used for water treatment. It is a very good performing system.
Membranes were first used in water treatment processes in the 1960s, but they became increasingly popular in desalination over the next decade.
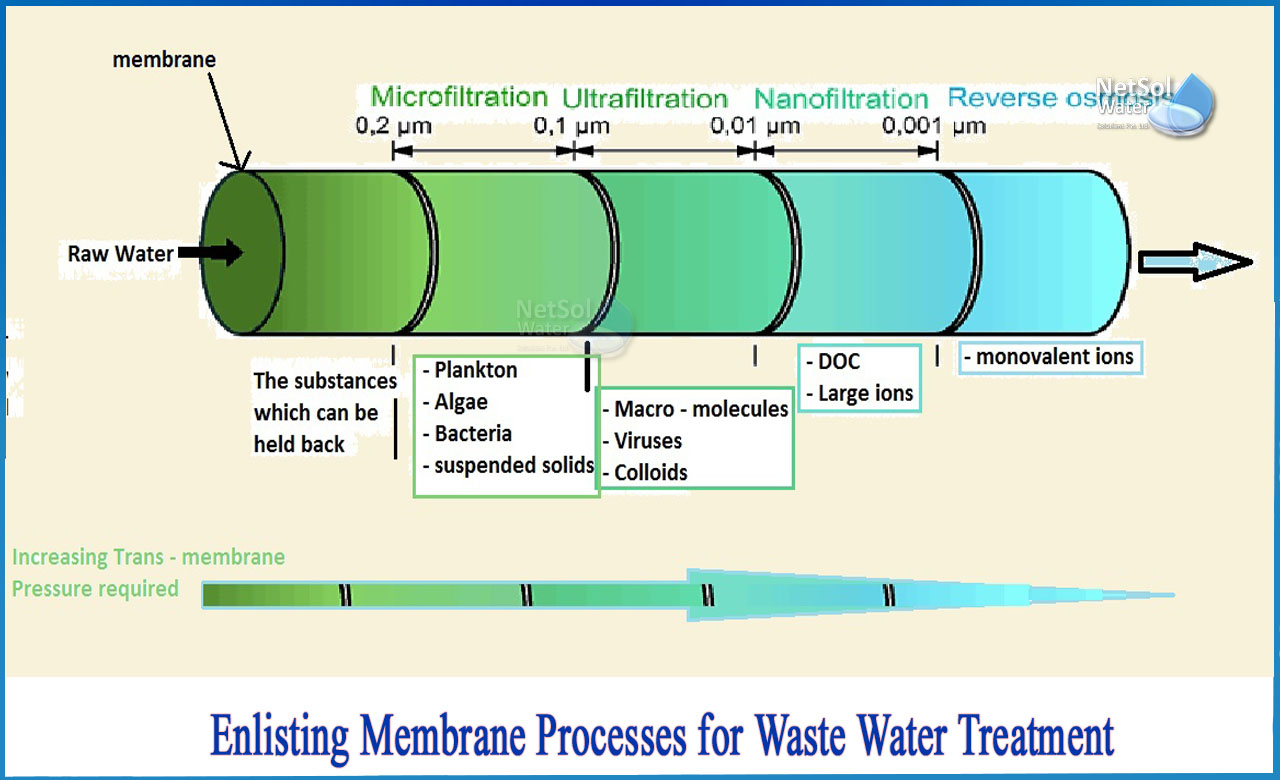
The following membrane processes are now included in the list of water treatment membrane processes:
· Forward osmosis
· Osmosis (reverse osmosis)
· Microfiltration
· Ultrafiltration
· Nanofiltration
Different processes necessitate different types of membranes, which, in general, serve as a sieve or separate water from impurities on a molecular level. Polymer-based films, ceramics, and other materials are used to create membranes. Materials block polymers, aluminum oxide, graphene, and other nanomaterials such as carbon nanotubes are being studied. The permeability of membranes varies.
Membrane Configurations and Types
Membranes are typically classified as either isotropic or anisotropic. Isotropic membranes have a uniform composition and physical structure in cross-section, whereas anisotropic membranes do not. They are typically made up of variously structured layers and materials. Tubular, hollow-fiber, and flat-sheet membranes are the most common types of membranes.
The following are the ideal properties of water treatment membrane configurations:
· Compactness
· Tangential flow resistance is low.
· Without dead zones, the velocity distribution is uniform.
· High retentate-side turbulence to aid mass transfer and reduce fouling.
· Simple upkeep and cleaning
· Low unit price
1. Plate-and-frame: The most basic configuration, consisting of two end plates, a flat sheet membrane, and spacers. The membrane is frequently on the inside of a tube in tubular modules, and the feed solution is pumped through the tube.
2.SPIRAL WOUND:The spiral wound module is the most commonly used module in industry for nanofiltration or reverse osmosis membranes. A flat sheet membrane is wrapped around a perforated permeate collection tube in this module. The feed is directed to one side of the membrane. Permeate collects on the other side of the membrane and spirals in towards the collection tube in the Centre.
3. Hollow fine fibers:Hollow fiber modules for seawater desalination are made up of bundles of hollow fibers housed in a pressure vessel. They can have a shell-side feed configuration, in which the feed runs along the outside of the fibers and exits at the ends of the fibers. Hollow fiber modules can also be used in bore-side feed configurations, in which the feed is circulated through the fibers. Hollow fibers, which are commonly used in wastewater treatment and membrane bioreactors, are not always used in pressure vessels. Bundles of fibers can be suspended in the feed solution, and permeate can be collected from one end of the fibers.
4. Tubular membranes: Porous tubes with inner diameters ranging from 5mm to 15mm are coated on the inside or outside walls with micro porous layers of PVDF or PES. Tubular modules, which are made up of individual tubular membranes fitted into a cylindrical housing, can be operated in either outside-in (waste water stream flowing outside individual tubes) or inside-out (waste water stream flowing inside individual tubes) configurations, depending on the orientation of the micro-porous layer.
5. Vibratory membranes:The main difference between traditional membranes and other separation systems is that the basic design is vertical rather than horizontal, which means that the space required per unit is less than for other separation systems.
These vibrating membranes can filter any type of wastewater and treat effluents with a high solids load. Furthermore, it is a technology that does not require chemicals to operate, with the exception of those required for periodic membrane cleaning.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.