How to design ETP plant for FMCG?
FMCG's full form is Fast Moving Consumer Goods, also known as Consumer Packaged Goods. They are among the most popular items on the market and are made specifically to meet the requirements of the average person on a daily basis. Consumer products, which are used by almost everyone on the earth and are frequently consumed, require frequent purchases from customers. They sell quickly and for cheap prices per unit since they have a limited shelf life.
The fast-moving consumer goods industry contributes to a substantial rise in waste. The usage of harsh chemical compositions, plastics, and single-use product packaging are the main causes. Due to the product's harmful raw components, waste is produced both during packing and after consumption.
In this blog, we will discuss in brief the working of ETP for FMCG Sector.
Working function of ETP for FMCG Sector:
Pre-treatment: as part of the pre-treatment process, to screen out any big solids or particles that might be present in the wastewater. The wastewater is then run through a grit chamber to remove any sand, gravel, or other heavy objects.
Primary treatment: The majority of solids are removed at the initial phase of treatment using screens and settling tanks. Given that solids account for around 35% of the contaminants that must be eliminated, this phase is crucial. The screens typically feature 10 millimetre-wide apertures, which are sufficiently narrow to filter out big objects like sticks, trash, and other debris from wastewater. This material is removed and disposed of at the landfill.
Secondary treatment: Bacteria are used in secondary wastewater treatment to break down the residual contaminants. This is done by vigorously combining bacteria and oxygen with wastewater. The oxygen speeds up the bacteria's digestion of the contaminants. The water is then transferred to settling tanks where the sludge once more settles, removing 90 to 95 percent of the contaminants from the water. About 90 to 99 percent of the coliform bacteria are eliminated by secondary treatment, along with 85 to 90 percent of BOD and suspended solids.
Tertiary treatment: The removal of dissolved materials during tertiary (or advanced) treatment includes the removal of color, metals, organic compounds, and nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen. Tertiary treatment involves a variety of physical, chemical, and biological therapeutic procedures.
Zero liquid discharge (ZLD): This method aims to flush a system of all liquid waste. ZLD focuses on producing clean water that may be used again (for example, irrigation), reducing wastewater in an inexpensive manner, and protecting the environment.
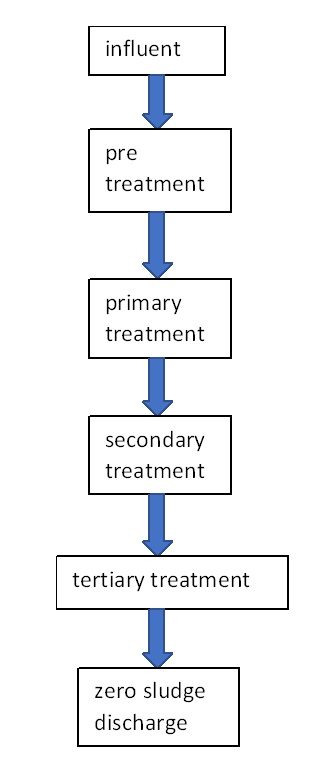
Process flow diagram of ETP for FMCG Sector
Do you need an advice or assistance on selecting the best water and waste water treatment unit? We have solutions for all your problems!
Let us now your problem, our experts will make sure that it goes away.
For an assistance or related query,
Call on +91-965-060-8473
Or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com



