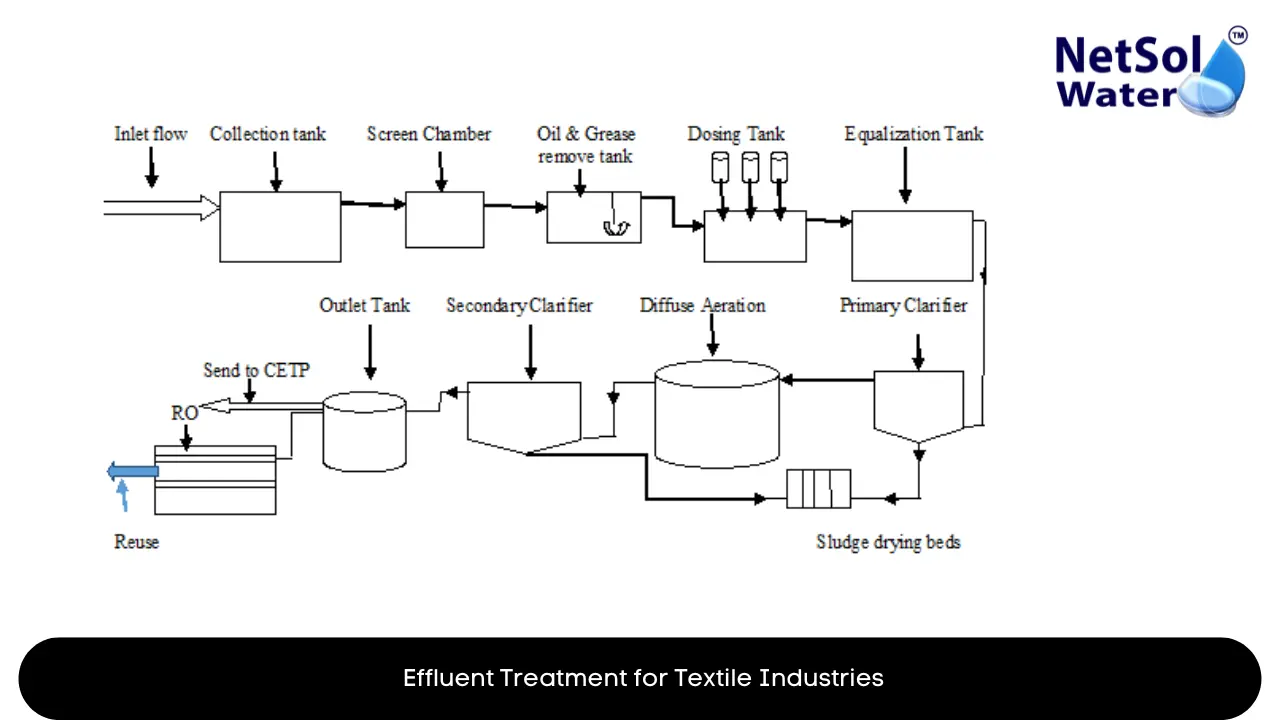
Effluent Treatment for Textile Industries
The textile industry is one of the most water-intensive sectors, utilizing substantial volumes for processes like de-sizing, scouring, bleaching, mercerising and dyeing. The resultant effluents are often highly coloured, turbid and laden with toxic organic and inorganic pollutants. Untreated textile effluent discharges pose severe ecological risks to receiving water bodies and land environments. Stringent regulations mandate appropriate treatment to ensure compliance with quality standards before discharge or reuse.
Let's explores the key treatment approaches implemented specifically for handling challenging textile effluents. We also discuss trends and innovations aimed at optimising treatment performance while promoting sustainability.
Characterizing Textile Effluents
Textile wastewaters vary considerably based on the fibres, dyes, process chemicals and unit operations involved. However, some common problematic parameters include:
High Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)
From salts, surface preparation agents and dye auxiliaries.
Intense Colour and Recalcitrant Dyes
Residual reactive dyes, disperse dyes, sulfur dyes and their breakdown products.
High Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)
Due to sizing agents, starch, waxes, fats and other organics present.
Fluctuating pH ranges
Ranging from highly acidic to alkaline effluents from different processes.
Presence of toxic metals and organics
Like chromium, lead, zinc, phenols and aromatics from certain dyes/processes.
Typical Treatment Processes:
An effective textile effluent treatment plant (ETP) incorporates:
Equalization and Neutralization
To balance fluctuating pH, flows and pollutant concentrations through holding tanks/basins.
Coagulation and Flocculation
For destabilizing and aggregating dispersed dye particles, metals using lime, alum, ferric salts.
Primary Clarification
Removing settleable solids, sludge through gravity separation in clarifiers/thickeners.
Secondary Biological Treatment
Aerobic bacterial degradation in activated sludge reactors for reducing BOD/COD levels.
Tertiary Treatment
Polishing effluent using membrane filtration, activated carbon or advanced oxidation for color/toxin removal.
Sludge Treatment and Disposal
Handling concentrated sludges/solids through dewatering, stabilization for reuse or disposal.
Emerging Innovations
Recent advances are tackling challenges like high dissolved solids, color persistence and sludge volumes:
Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs)
Integrating activated sludge with membrane filtration in a sub-merged configuration for enhanced organics removal.
Electrochemical Oxidation
Using electrode materials like boron-doped diamond for electro-oxidizing recalcitrant toxic dyes.
Enzymatic Treatments
Employing enzymes like laccases and peroxidases from white-rot fungi for dye degradation.
Forward/Reverse Osmosis
Deploying advanced membrane separation for concentrating and recovering high TDS streams.
Evaporation Systems
Utilizing multi-effect evaporators or membrane distillation for zero liquid discharge through water recovery.
Valorisation of Textile Wastes
Extracting valuable products like pigments, enzymes, biosurfactants, and recovered salts from effluents.
Textile companies increasingly view sustainable water and waste management as integral to maintaining competitiveness. Besides treatment for compliance, recovering water and valorising effluent streams presents circular economy opportunities.
Conclusion
With their complex composition and high dissolved solids content, textile industry effluents pose a unique challenge for treatment. An integrated approach combining physical, biological and chemical processes is imperative. As textile manufacturing grows, conventional treatment plants are being optimized through process intensification. However, the long-term solution lies in adopting innovative treatment methods focused on effluent valorization, minimizing sludge disposal and facilitating water reuse/recovery.
Close collaboration between textile companies, technology providers, environmental agencies and financiers is key. It can unlock sustainability while giving textile effluent treatment a lucrative role in the circular economy vision.
To explore customised commercial RO plants, Industrial RO plants, ETP or STP solutions for your needs in your areas and nearby regions, contact Netsol Water at:
Phone: +91-965-060-8473
Email: enquiry@netsolwater.com