Designing an Effluent Treatment Plant for Coal Mines
Coal mining is an important economic activity in many parts of the world. However, it is also known to generate significant amounts of effluent or wastewater, which can be harmful to the environment and public health if not properly treated. To mitigate this, effluent treatment plants (ETPs) are designed and constructed to treat and discharge the effluent safely.
Here we will focus on designing an effluent treatment plant for coal mines, including the design basis, process flow diagram, and working functions.
Design Basis
The design basis for an effluent treatment plant for coal mines is determined by the characteristics of the effluent generated, including its quantity, quality, and composition. Typically, the effluent generated from coal mines contains suspended solids, heavy metals, and organic compounds. The effluent's quantity and flow rate depend on the mining operation's scale, while the effluent's composition varies depending on the type of coal and the location of the mine.
The factors that may affect the design of an Effluent treatment plant for Coal mines are enumerated below:
1. Discharge being acidic or alkaline in nature?
2. Presence of iron, sulfate or aluminum
3. The degree of gypsum crystallization that occurs in the primary neutralization plant and in the coal processing plant.
4. The effect of gypsum crystallization on the gypsum saturation index after separate and joint treatment of different mine water streams.
5. The optimal sulphate removal method to achieve a low operating scaling index (OSI) value for coal beneficiation plant use.
6. The possibility of pre-washing the coal to reduce the capital and running cost of the treatment plant.
7. The compliance with the Coal Mining Effluent Guidelines and Standards set government.
Process Flow Diagram
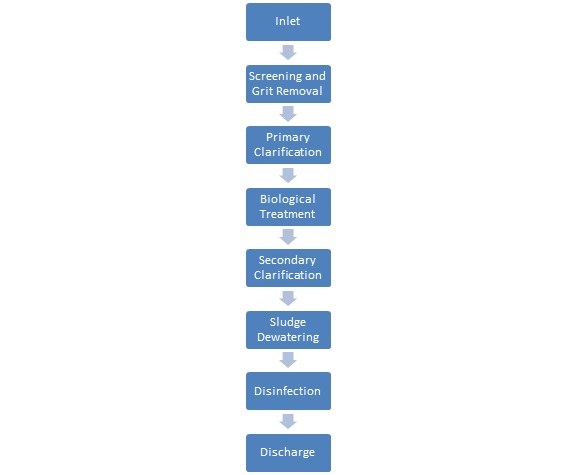
The process flow diagram for an effluent treatment plant for coal mines consists of several unit operations designed to treat the effluent in a series of steps. The following are the steps involved in treating the effluent:
Working Functions
The effluent treatment plant for coal mines operates based on the principles of physical, chemical, and biological treatment. The following are the functions of the different unit operations:
· Screening and Grit Removal: The effluent from coal mines is usually mixed with sand, gravel, and other debris. The first step in treating the effluent is to remove the coarse solids, including sand and gravel, through screening and grit removal. The screening is done using a series of screens with different mesh sizes to remove different-sized particles. The grit removal process involves the use of settling tanks or grit chambers to allow the heavy particles to settle at the bottom.
· Primary Clarification: The effluent is then directed to the primary clarifier, where the finer solids settle to the bottom of the tank, forming sludge. The sludge is then removed through a sludge removal system. The clarified effluent is then transferred to the next stage. In other words, the primary clarifier removes the finer solids that settle in the effluent, reducing the load on the biological treatment system.
· Biological Treatment: The clarified effluent is then directed to a biological treatment system, where microorganisms break down the organic compounds in the effluent. The biological treatment system can be an activated sludge process, a trickling filter process, or a combination of both.
In this unit operation, microorganisms break down the organic compounds in the effluent, reducing its chemical oxygen demand (COD) and biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) levels.
· Secondary Clarification: The effluent from the biological treatment system is then directed to a secondary clarifier, where the remaining suspended solids settle to the bottom of the tank. The settled solids are removed through a sludge removal system, and the clarified effluent is then ready for discharge.
· Disinfection: Before discharge, the effluent is treated with disinfectants such as chlorine or ozone to kill any remaining bacteria or viruses.
Summary:
Designing an effluent treatment plant for coal mines is essential to ensure that the effluent generated from mining operations does not harm the environment or public health. The design basis for such a plant is determined by the characteristics of the effluent generated, including its quantity, quality, and composition. The process flow diagram for an effluent treatment plant for coal mines consists of several unit operations, including screening and grit removal, primary clarification, biological treatment, secondary clarification, and disinfection. These unit operations operate based on the principles of physical, chemical, and biological treatment, with the aim of reducing the effluent's pollutant levels and ensuring its safety before discharge.
Leading manufacturer of sewage treatment plants in India.
Netsol Water is the leading manufacturer, supplier, and exporter of a quality selection of water treatment, and wastewater treatment products in India, by using advanced sewage treatment methods.
RO plants, water softeners, ETPs, STPs, DM plants, AMC, O&M, Ultra filtration, UV, Ozonation, ZLD plants, Anoxic tanks, and other goods and services are available from us. We also provide services to businesses in sectors including automotive, pharmaceutical, textile, pulp & paper, beverages, refineries, schools, hospitals, office buildings, and hotels, among others.
Call us at +91 9650608473 or email at enquiry@netsolwater.com for further information.



