Designing an ETP for Glass Industry: A Step-by-Step Guide
Glass manufacturing is a complex process that involves the use of various chemicals and produces a significant amount of wastewater. This wastewater, also known as effluent, can contain hazardous pollutants that require treatment before discharge into the environment.
Let us begin to discuss the design process of an effluent treatment plant (ETP) for a glass industry, including the process flow diagram and the working function in detail.
Design Process:
The design process of an ETP involves several steps, including:
Step 1: Characterization of Effluent
The first step in designing an ETP is to characterize the effluent. This involves analyzing the composition of the effluent to determine the type and concentration of pollutants present. The analysis should include parameters such as pH, total dissolved solids (TDS), chemical oxygen demand (COD), biological oxygen demand (BOD), and heavy metals.
Step 2: Process Selection
Once the effluent has been characterized, the next step is to select the appropriate treatment process. The selection of the process will depend on the type and concentration of pollutants present in the effluent. Some common treatment processes include physical, chemical, and biological treatment.
Step 3: Design Parameters
After selecting the treatment process, the design parameters must be determined. These parameters include the hydraulic retention time (HRT), organic loading rate (OLR), and the size of the treatment units. The HRT is the time that the effluent remains in the treatment unit, while the OLR is the amount of organic matter that can be treated in a given time.
Step 4: Design Calculations
With the design parameters determined, the next step is to calculate the size of the treatment units. This includes determining the dimensions of the reactor, the volume of the reactor, and the amount of media required. The design calculations will depend on the selected treatment process.
Type of Effluent:
The ETP for a glass industry may have to deal with high levels of silica, fluoride and heavy metals in the effluent
Process:
The process flow diagram below shows the process.
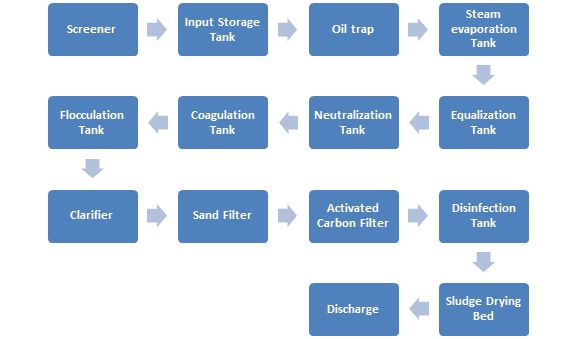
Working Function:
The working function of an ETP involves generally several treatment units, each with a specific function. Some common treatment units include:
1. Screener
Screening is necessary to trap the big objects like paper , woods parts , clothes , Cary bags and metals parts too. Screening is first operation which is used in Effluent treatment plant . We need select a proper MOC of screening as per effluent pH value or crossvines .
2. Input Storage Tank
This tank is used to store the raw effluent coming from different areas of the glass plant. The effluent is mixed and homogenized in this tank. The tank also acts as a buffer for variations in flow rate and quality of effluent.
3. Oil trap
Oil trap is used to separate oil and grease from the effluent. The oil and grease float on the surface of the water and are skimmed off by a scraper mechanism. The oil and grease are collected in a separate tank for further disposal or recovery.
4. Steam evaporation Tank
Steam evaporation tank is used to evaporate water from the effluent and reduce its volume. The steam generated from the tank can be used for heating or power generation purposes. The concentrated effluent is sent to the next stage of treatment.
5. Equalization Tank
Equalization tank is used to maintain a constant flow rate and quality of effluent for the subsequent treatment processes. The tank also provides aeration and mixing of the effluent to prevent settling of solids and odour formation.
6. Neutralization Tank
Neutralization tank is used to adjust the pH of the effluent to a desired range by adding acid or alkali. The pH of the effluent affects the efficiency of coagulation, flocculation and biological treatment processes.
7. Coagulation Tank
Coagulation tank is used to add coagulants such as alum, ferric chloride or lime to the effluent. The coagulants react with the dissolved and suspended solids in the effluent and form larger particles called flocs.
8. Flocculation Tank
Flocculation tank is used to add flocculants such as polyelectrolytes or organic polymers to the effluent. The flocculants enhance the aggregation of flocs and increase their settling velocity.
9. Clarifier
Clarifier is used to separate the flocs from the clear water by gravity settling. The flocs settle at the bottom of the clarifier and are removed by a sludge scraper mechanism. The clear water overflows from the top of the clarifier and is sent to the next stage of treatment.
10. Sand Filter
Sand filter is used to remove any remaining suspended solids from the clear water by passing it through a bed of sand media. The sand media traps the solids and allows the filtered water to pass through.
11. Activated Carbon Filter
Activated carbon filter is used to remove any dissolved organic matter, colour, odour and taste from the filtered water by adsorption on activated carbon media. The activated carbon media has a large surface area and high affinity for organic molecules.
12. Disinfection Tank
Disinfection tank is used to kill any pathogenic microorganisms present in the disinfected water by adding disinfectants such as chlorine, ozone or ultraviolet radiation. The disinfection process ensures that the treated water is safe for reuse or discharge into the environment.
13. Sludge Drying Bed
Sludge drying bed is used to dewater and dry the sludge generated from various treatment processes. The sludge is spread over a bed of sand or gravel and allowed to drain by gravity. The dried sludge can be disposed of in a landfill or used as a fertilizer or fuel source.
Summary:
Designing an effluent treatment plant for a glass industry requires careful consideration of the effluent composition and treatment process selection. The design process involves several steps, including effluent characterization, process selection, design parameters, and design calculations. The process flow diagram and working function provide a visual representation of the treatment process and help identify potential issues. Proper design and operation of an ETP can significantly reduce the environmental impact of the glass industry.
Leading effluent treatment plants manufacturer in India.
Netsol Water is the leading manufacturer, supplier, and exporter of a quality selection of water treatment, and wastewater treatment products in India, by using advanced sewage treatment methods.
RO plants, water softeners, ETPs, STPs, DM plants, AMC, O&M, Ultra filtration, UV, Ozonation, ZLD plants, Anoxic tanks, and other goods and services are available from us. We also provide services to businesses in sectors including automotive, pharmaceutical, textile, pulp & paper, beverages, refineries, schools, hospitals, office buildings, and hotels, among others.
Call us at +91 9650608473 or email at enquiry@netsolwater.com for further information.



