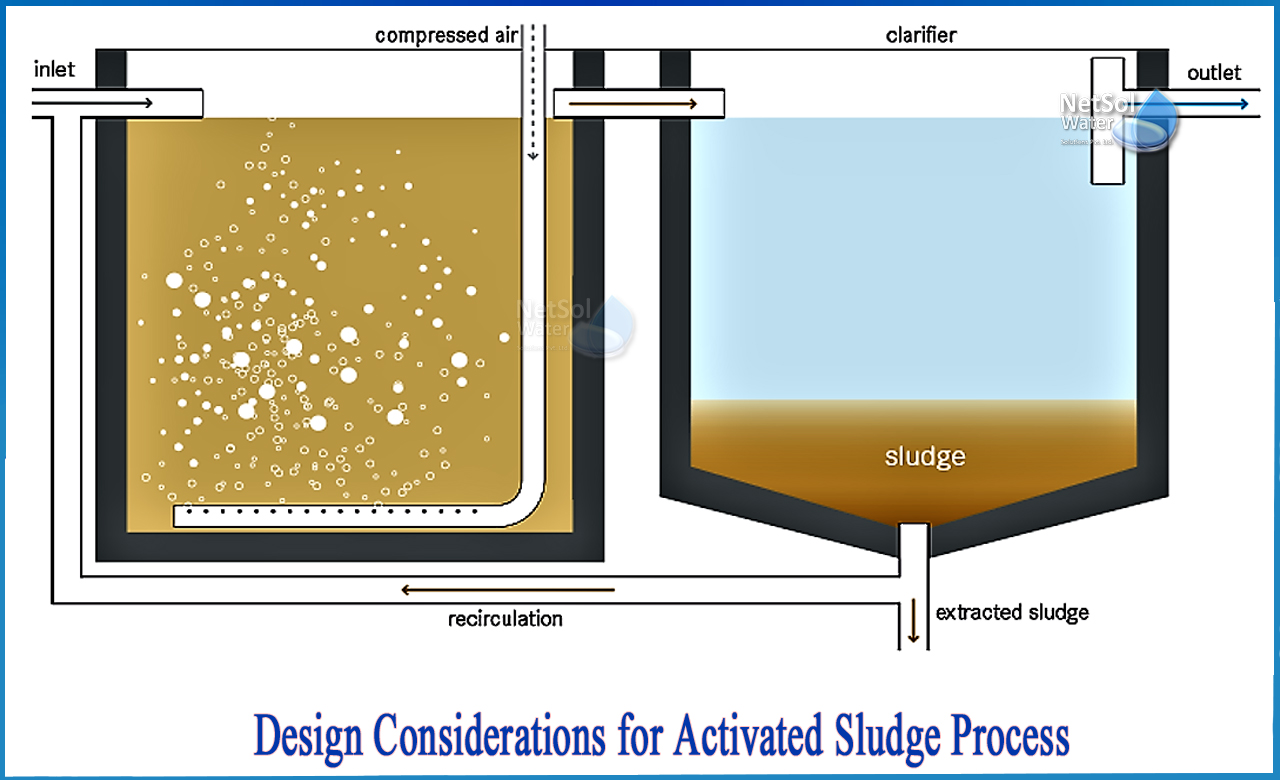
What are the various design parameters of activated sludge process?
Aeration tank capacity and dimensions, aeration facilities, secondary sludge settling and recycling, and excess sludge squandering are all factors to consider while designing an activated sludge facility.
1-Tank for aeration:
The capacity of the aeration tank is estimated for the chosen θc by assuming a sufficient MLSS concentration, X.
VX= YQθc(SO-S) / (1+kdθc)
Alternatively, the tank capacity might be calculated using
F/M = QSO / XV
As a result, the first step in designing is to select an appropriate value of θc (or F/M), which is determined by the projected winter temperature of the mixed liquor, the kind of reactor, the estimated settling properties of the sludge, and the amount of nitrification required. When nitrification is sought together with effective BOD removal and full mixing systems are used, the option normally ranges from 5 days in warmer areas to 10 days in temperate countries.
The second step is to select two interrelated parameters HRT, t and MLSS concentration.Consequently, it is seldom assumed to be greater than 5000 g/m3.
The MLSS value for ordinary home sewage is 2000-3000 mg/l if a standard plug flow type aeration system is used, or 3000-5000 mg/l for entirely mixed kinds. The tank's length is determined by the kind of activated sludge plant. The aeration tanks, with the exception of extended aeration plants and entirely mixed plants, are constructed as long narrow channels.
The width and depth of the aeration tank are determined by the aeration equipment used. The depth, which typically varies from 3 to 4.5 m, controls the aeration effectiveness. The mixing is controlled by the breadth, which is typically kept between 5 and 10 m. The width-depth ratio should be set between 1.2 and 2.2. The length should not be less than 30 m and should not be more than 100 m.
2-Secondary sludge settling tank:
Zone or compression settling occurs in secondary settling tanks that receive biologically treated flow. Beyond a particular concentration, zone settling occurs when the particles are close enough together that interparticulate forces hold the particles fixed relative to one another, causing the entire mass to settle as a single layer or "blanket" of sludge. If particles are in such concentration that they come into physical touch with one another, compression settling may occur at the tank's bottom. Beyond an MLSS concentration of 2000 mg/l, the solids loading rate, rather than the overflow rate, is generally used to regulate the clarifier design. Design values for processing household sewage in final clarifiers and mechanical thickeners are provided.
3-Reprocessed sludge/Sludge recycling:
The MLSS concentration in the aeration tank is determined by the sludge recirculation rate as well as the secondary sedimentation tank's sludge settleability and thickening.
Qr = X
Q Xr-X
WhereQr = Sludge recirculation rate, m3/d
Sludge settleability is assessed by the sludge volume index (SVI), which is defined as the volume filled in mL by one gramme of solids in the mixed liquid after 30 minutes of settling. If the sedimentation of suspended particles in the laboratory is considered to be identical to that in the sedimentation tank, then
Xr = 106/SVI.
SVI values of 100 to 150 ml/g suggest excellent settling of suspended solids. The Xr value must not exceed 10,000 g/m3 unless additional thickeners are installed to concentrate the settled solids or a secondary sedimentation tank is constructed to provide a greater value.
4-Excess of sludge wasting:
To maintain a constant level of MLSS in the system, the sludge in the aeration tank must be squandered. The amount of surplus sludge increases with rising F/M and decreases with increasing temperature.
Excess sludge can be discarded as mixed liquor either through the sludge return line or directly from the aeration tank. The latter is favoured since the sludge content is rather constant. The surplus sludge created during steady-state operation may be calculated using:
θc = VX
QwXr
Or QwXr = YQ (SO - S) - kd XV
Contact Netsol Water for more information!
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.