Best STP Technology for cold areas like Jammu and Kashmir
Sewage treatment plants (STPs) are critical infrastructure for ensuring clean and safe water in populated areas. However, in cold regions like Jammu and Kashmir and other areas around the world, STPs must be designed to operate efficiently in low temperatures.
Here we will discuss the most efficient STP technology for cold regions, its design process, process flow diagram, working function, and advantages over other technologies.
Different Technologies:
There are different types of technologies that can be used for sewage treatment plants, depending on various factors such as the quality of wastewater, the environmental conditions, the energy consumption, the space availability and the cost-effectiveness.
Some of the common technologies are: -
1. Membrane Bio-Reactor (MBR):
This technology uses a biological process to treat wastewater, followed by a membrane filtration module that removes suspended solids and microorganisms. MBR produces high-quality effluent that can be reused without further treatment.
However, it also has some disadvantages such as high energy consumption, high capital and operational costs, and complex maintenance
2. Moving Bed Bio Reactor (MBBR):
This technology uses plastic media that provide a large surface area for bacteria to grow and degrade organic matter in wastewater. MBBR requires lower footprint and is easy to operate and maintain compared to conventional activated sludge processes.
However, it also has some disadvantages such as varying design criteria, quality of plastic media, and mixing issues
3. Thermal Hydrolysis:
This technology uses high temperature and pressure to break down organic matter in sludge and produce biogas that can be used for energy generation. Thermal hydrolysis reduces the amount of sludge and improves its dewaterability and digestibility.
However, it also has some disadvantages such as high capital and operational costs, corrosion issues, and safety risks. For cold areas, the choice of technology may depend on the specific challenges
Technology: MBR (Membrane Bioreactor)
The Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) technology is one of the most efficient STP technologies for cold regions. MBRs combine biological treatment with membrane filtration, resulting in a high-quality effluent that is suitable for reuse or discharge.
Design Process:
The design process for an MBR-based STP in cold areas is as follows:
1. Determine the Design Flow:
The first step in designing an MBR-based STP is to determine the design flow rate, which is based on the population served by the plant.
2. Determine the Size of the Bioreactor:
The size of the bioreactor is determined based on the design flow rate and the desired hydraulic retention time (HRT).
3. Determine the Membrane Filtration System:
The membrane filtration system is critical in ensuring that the treated wastewater is free of impurities. In cold areas, submerged membranes are recommended, as they provide better filtration efficiency.
4. Determine the Sludge Treatment System:
The sludge generated during the treatment process requires further treatment before disposal. In cold areas, aerobic digestion is the most common method of sludge treatment.
5. Determine the Tertiary Treatment System:
The treated wastewater undergoes tertiary treatment to remove any remaining contaminants, including nutrients and pathogens. In cold areas, ultraviolet disinfection is a common method of tertiary treatment.
Process Flow Diagram:
The following process flow diagram illustrates the MBR-based STP design process in cold areas:
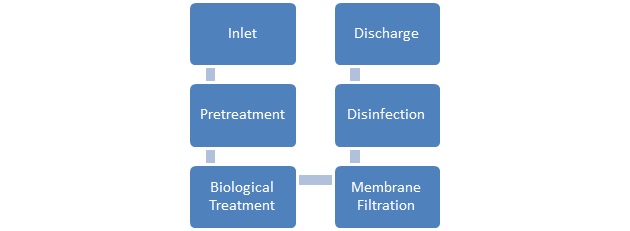
Working Function:
The MBR-based STP operates as follows:
1. Pretreatment: The wastewater is pretreated to remove any large particles, including debris and sediment.
2. Biological Treatment: The wastewater is then introduced into the bioreactor, where aerobic bacteria break down the organic matter.
3. Membrane Filtration: The treated wastewater is then passed through a membrane filtration system, which removes any remaining impurities.
4. Disinfection: The treated wastewater is disinfected using ultraviolet light to remove any remaining pathogens.
5. Reuse or Discharge: The treated wastewater can be reused for non-potable purposes or discharged into a water body.
Advantages of MBR Technology:
The MBR technology offers several advantages over other STP technologies, especially in cold areas. Some of these advantages include:
· High-Quality Effluent: The MBR technology produces high-quality effluent that is suitable for reuse or discharge.
· Space Efficiency: The MBR technology requires less space than other STP technologies, making it suitable for areas with limited space.
· Flexibility: The MBR technology can handle variable flow rates and can be easily adjusted to suit the treatment requirements.
· Energy Efficiency: The MBR technology requires less energy than other STP technologies, as it operates at a lower hydraulic loading rate.
Summary:
The Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) technology is the most efficient STP technology for cold regions like Jammu and Kashmir. Its combination of biological treatment and membrane filtration, coupled with its high-quality effluent, space efficiency, flexibility, and energy efficiency, make it ideal for these regions. When designing an MBR-based STP, the design flow rate, size of the bioreactor, membrane filtration system, sludge treatment system, and tertiary treatment system
Leading manufacturer of sewage treatment plants in India.
Netsol Water is the leading manufacturer, supplier, and exporter of a quality selection of water treatment, and wastewater treatment products in India, by using advanced sewage treatment methods.
RO plants, water softeners, ETPs, STPs, DM plants, AMC, O&M, Ultra filtration, UV, Ozonation, ZLD plants, Anoxic tanks, and other goods and services are available from us. We also provide services to businesses in sectors including automotive, pharmaceutical, textile, pulp & paper, beverages, refineries, schools, hospitals, office buildings, and hotels, among others.
Call us at +91 9650608473 or email at enquiry@netsolwater.com for further information.



