What is activated sludge process explain in details?
Activated sludge process (ASP) and Trickling Filter are two examples of traditional biological wastewater treatment under aerobic conditions. In 1914, the ASP was created in England.
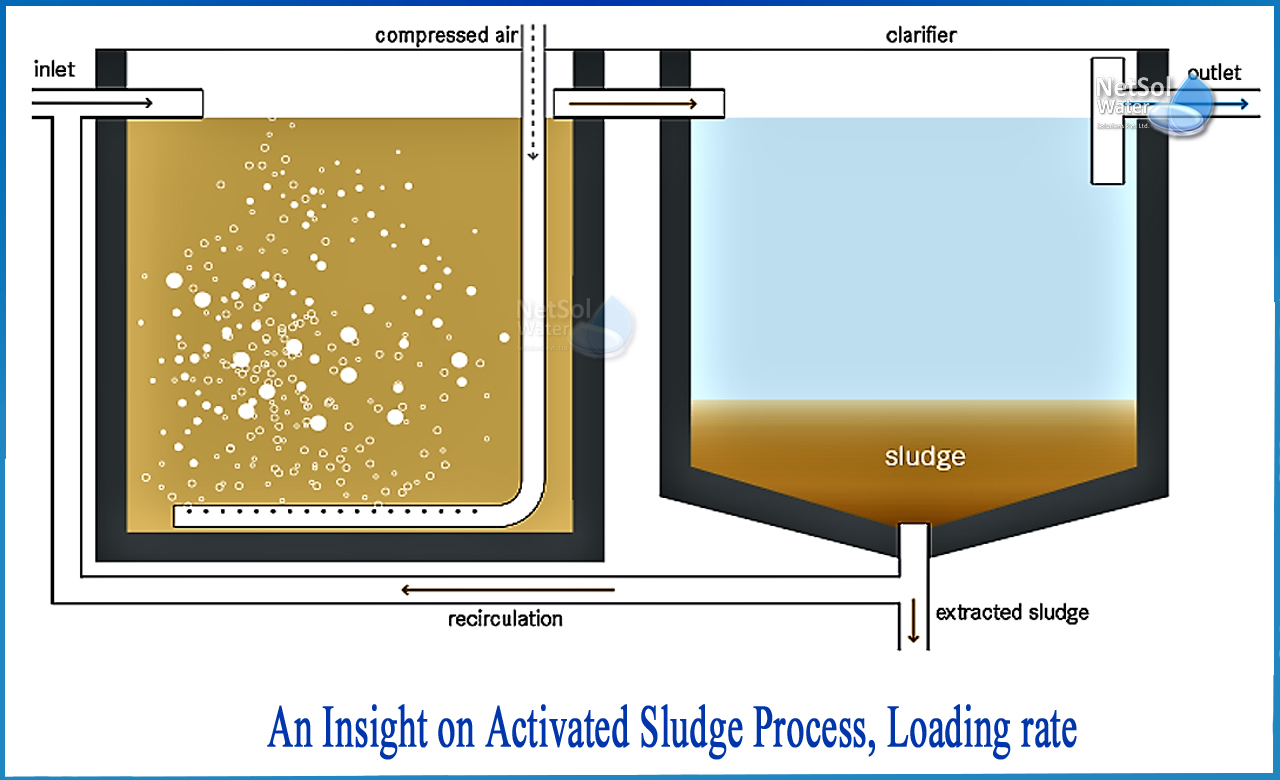
Organic matter is stabilized by bacteria under aeration in the activated sludge process of an aeration tank, and in a secondary sedimentation tank (SST),the biological cell mass is separated from the aeration tank effluent, and the settled sludge is recycled partly to the aeration tank and the rest is wasted.
The activated sludge process necessitates recycling. Diffused or mechanical aeration is utilized to produce the desired aeration conditions.
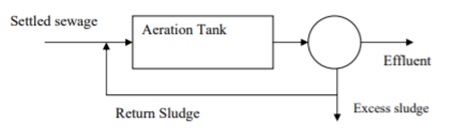
Conventional Activated Sludge Process
Diffusers can be installed at the tank's bottom, and mechanical aerators are installed on the water's surface, either floating or permanent. In the event of diffused air aeration, settled raw wastewater and returning sludge enter the tank's head and traverse the tank in a spiral flow pattern, or get totally mixed in the case of a completely mixed reactor. In the case of a plug flow aeration tank, the air supply can be tapered throughout the length to match the amount of oxygen demand. In the settling tank, the effluent settles, and the sludge is returned at a fixed pace.
What is Loading Rate?
The organic matter loading rate applied to the reactor is measured in kilograms of BOD per unit volume of the reactor per day, known as volumetric loading rate, or kilograms of BOD per day per unit mass of microorganisms present in the reactor (i.e. in the aeration tank), known as organic loading rate or F/M.
The following formula may be used to compute volumetric loading:
‘Volumetric loading = BOD x Q x 10-3/ Vol’

The F/M ratio is the most important component in BOD elimination. Higher BOD removal will be achieved with lower F/M levels. Changing the MLVSS concentration in the aeration tank can change the F/M.
What is MCRT (Mean Cell Residence Time) or (SRT) Solid Retention Time?
Period during whichmicrobial mass is kept in the system determines the Activated sludge processes efficacy in terms of organic matter removal.
The sludge's retention in the SST is determined by the sludge's settling rate. Appropriate recirculation of the sludge in the aeration tank may be feasible, if the sludge settles well in the SST, which aid in the system's SRT being maintained. Otherwise, if the sludge has weak settling qualities, it will not settle in the SST which makes recirculation difficult and perhaps lowering the system's SRT.
The SRT may be calculated as follows:
SRT = kg of MLVSS in aeration Tank/ (kg of VSS wasted per day + kg of VSS lost in effluent per day)
The VSS lost in the effluent is usually overlooked because it is such a minor quantity compared to the artificial squandering of sludge from the sludge recycling line or the aeration tank.
What is Sludge Volume Index?
The volumetric quantity of return sludge is determined after 30 minutes of settling.
The sludge volume index (SVI) is the volume of the sludge in mL for one gramme of dry weight of suspended solids (SS). The SVI ranges from 50 to 150 milliliters per gram of SS. Sludge settles easier when the SVI is lower.
Netsol can help!
Netsol Water is the leading name when it comes to wastewater treatment processes. Incorporating all the recent trends and technologies in our units, we have gained No.1 reputation in the market today. Customer satisfaction and value for the money is our motive.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.