What are the advantages and disadvantages of SBR?
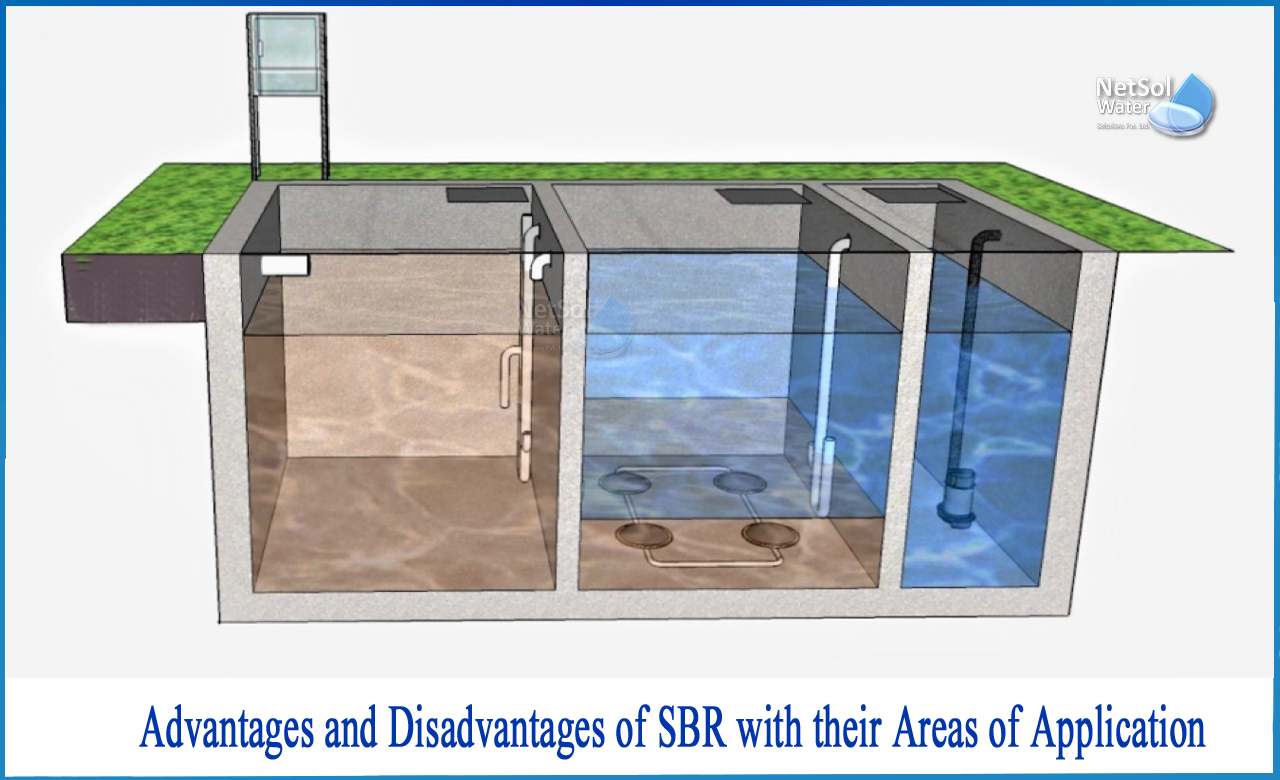
SBR is a wastewater treatment system that uses a fill-and-draw activated sludge technology.
In this system, wastewater is pumped into a single "batch" reactor, where it is treated to eliminate contaminants before being released. A single batch reactor can be used for equalization, aeration, and clarifying. Two or more batch reactors are employed in a specified sequence of operations to improve the system's performance.
Stages in Sequencing Batch Reactors (SBR)
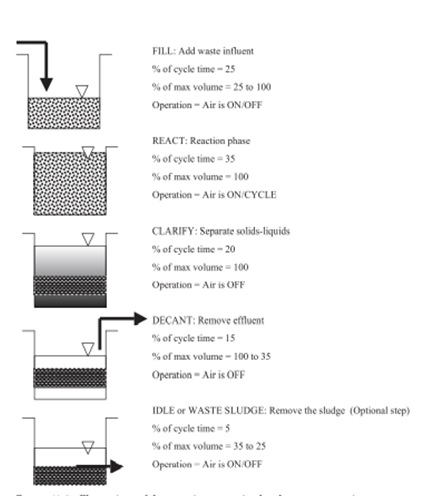
SBR treatment systems consist of a cycle of five stages: Fill, react, settle, draw and idle.
Applicability of Netsol’s range of SBR Systems
1: They're especially well-suited to low- or intermittent-flow wastewater treatment applications.
2: For the treatment of home and industrial wastewater, the sequencing batch reactor is a practical and adaptable option. It not only eliminates carbon dioxide, but also nitrogenous species and some biological nutrients. It has benefits over the so-called traditional activated sludge system from an economic and operational standpoint.
3: These systems are effective in regions where available land is limited since they have a tiny footprint. Furthermore, if nutrient removal becomes essential in the future, the system's cycles may be readily changed. As a result, SBRs are particularly adaptable to regulatory changes in effluent characteristics like nutrient removal. If additional treatment, like as filtering, is necessary, SBRs are also highly cost effective.
4: Separate and mixed municipal and industrial wastewater are effectively treated in SBR systems.
5: As with conventional activated sludge plants, SBRs can be used for all plant sizes.
Advantages and disadvantages of Sequencing Batch Reactors
a. Advantages of SBR Systems
i. Single vessel:One single reactor basin provides all of the unit operations and processes that require two separate basins in a conventional activated sludge plant configuration that can provide an effluent quality suitable for reuse. In most circumstances, a single reactor vessel can handle equalization, primary clarification, biological treatment, and secondary clarification.
ii. Operational flexibility and control:This process can be operated and controlled with flexibility for efficient removal of organic matter, suspended solids, nitrogen, and phosphorus under all loading conditions. It provides enhanced biological phosphorus removal with or without chemical augmentation.
iii. This process can control the growth of filamentous bacteria and prevent bulking of activated sludge.
iv. By eradicating the need for final sedimentation tanks, this method saves money in the long run. Due to the lack of supplementary sedimentation tanks in this process, the footprint space required is also modest, as simultaneous multiprocessing takes place in a single reactor basin (about 100m2 /1000m3 only required for SBR Tanks).
v. When the VSS:TSS ratio is large, SBR may be employed with main clarifiers and power generation arrangements.
vi. SBR allows for simple population increase through modular expansion. It's simple to handle modular setups and cycle operation to offer continuous input and outflow hydraulic profiles, eliminating the requirement for outflow hydraulic balancing.
b. Disadvantages of SBR Systems
i. Compared to the conventional activated sludge system, a higher level of maintenance can be associated with more automated switches and valves.
ii. Basin depth should be sufficient to provide an adequate clear water depth over the sludge blanket to prevent settled solids entrainment.
iii. In small SBR systems approximately less than 10 MLD, effluent flow balancing may be needed for downstream processing, such as filtration or disinfection.
iv. Short circuiting of influent conservative parameters (ammonia nitrogen, orthophosphate) under the non-interrupted inflow protocol may be a process failure consideration in some SBRs.
v. Larger capacity aeration system, relative to aeration time per cycle and per day, is required compared to conventional activated sludge system.
vi. In comparison to traditional activated sludge systems, bigger systems of timing units and controls necessitate a greater degree of sophistication.
vii. Some SBR systems have the potential to discharge floating or settled sludge during the decant phase.
viii. Depending on the aeration system utilized by the manufacturer, aeration devices may become plugged during certain working cycles.
ix. After the SBR process, equalization is required depending upon the downstream process such as filtration or disinfection.
x. There should be sufficient allowance of clear water depth from the sludge blanket to minimize sludge carryover. The volume of water decanted should be limited to prevent scouring of solids.
xi. All SBR plants must be designed to cater to peak flows. A minimum of two tank system is required.
xii. Extended aeration consumes a lot of power.
What can we offer?
Netsol Water is one of India's major water and wastewater management company, specialized in the design, manufacture, and delivery of custom-made treatment systems, industrial machinery, and luxury amenities for the water industry. We can customize STPs that will cater to all your needs and at the same time effectively treat different types of wastewater.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.