Activated Carbon Adsorption for Dye Removal in Textile Effluent Treatment Plants
The textile industry is an important part of our lives, giving us the clothes and fabrics we use every day. But, it also creates a lot of waste, especially wastewater full of artificial dyes. If we don't treat this wastewater properly, it can harm the environment and even make people and animals sick. What makes it worse is that many of these dyes are tough to break down naturally.
Conventional Treatment Methods: Limitations and Challenges
Textile effluent treatment has traditionally relied on methods such as coagulation, flocculation, and biological treatment. While these techniques can remove some of the pollutants, they often struggle to cope with the complex nature of dye molecules, leaving residual color and toxicity in the treated water. Additionally, some of these methods generate large volumes of sludge, posing disposal challenges and further environmental concerns.
The Promise of Activated Carbon Adsorption
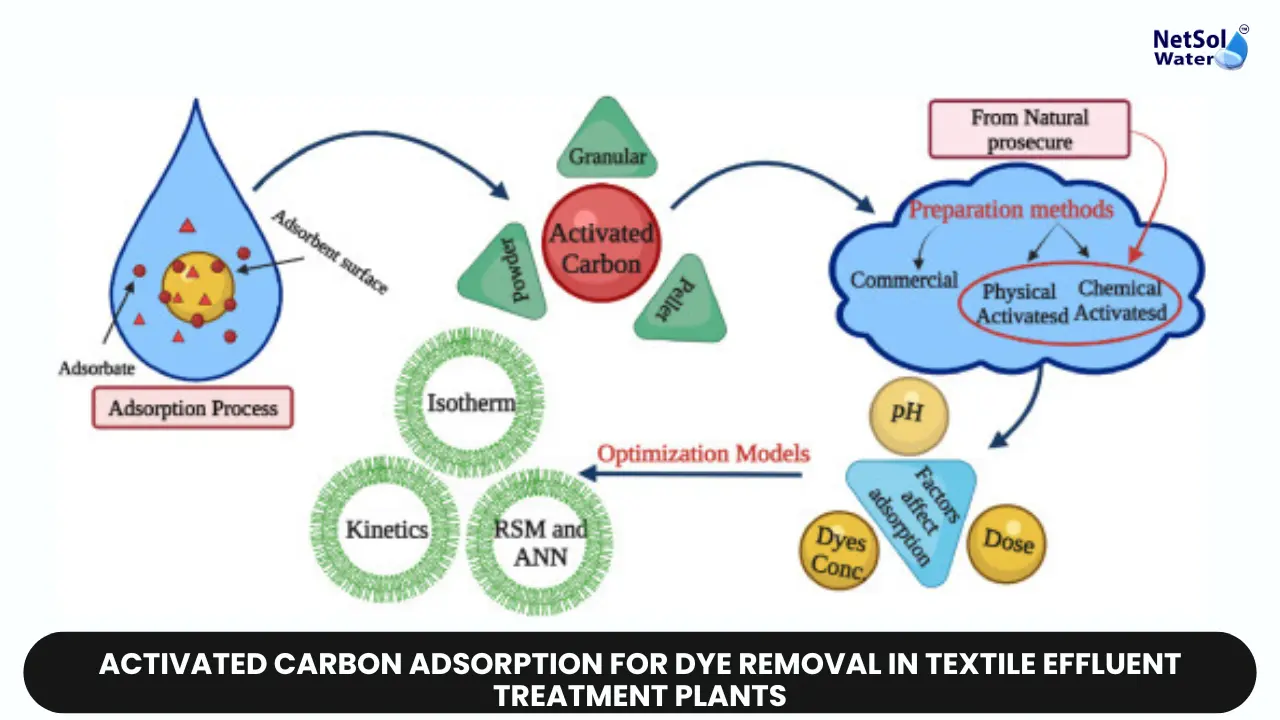
Adsorption using activated carbon has emerged as a promising solution for dye removal in textile effluent treatment plants. Activated carbon is a highly porous material with an exceptionally large surface area, making it an ideal adsorbent for a wide range of organic compounds, including dyes.
Mechanism of Adsorption
The adsorption process relies on the principle of attractive forces between the adsorbent (activated carbon) and the adsorbate (dye molecules). These forces can include van der Waals interactions, electrostatic attractions, and chemical bonding. When the textile effluent comes into contact with the activated carbon, the dye molecules are attracted to the carbon's vast surface area and become bound to it, effectively removing them from the water phase.
Activated Carbon Properties and Characteristics
The effectiveness of activated carbon as an adsorbent for dye removal depends on several factors, including its surface area, pore size distribution, and surface chemistry. Activated carbon with a high surface area and well-developed pore structure provides more adsorption sites, enhancing its capacity to remove dyes. Additionally, the surface chemistry of the carbon can be tailored to optimize its affinity for specific dye types through various activation methods and surface modifications.
Types of Activated Carbon
Activated carbon can be produced from a variety of carbonaceous materials, such as coal, wood, coconut shells, or agricultural waste. The choice of precursor material and activation process (physical or chemical) can influence the final properties of the activated carbon, including its adsorption capacity and selectivity towards different dye molecules.
Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherms
Understanding the adsorption kinetics and isotherms is crucial for optimizing the adsorption process and designing efficient treatment systems. Adsorption kinetics describe the rate at which dye molecules are adsorbed onto the activated carbon, while adsorption isotherms provide insights into the equilibrium distribution of dye molecules between the liquid and solid phases. These parameters are influenced by factors such as dye concentration, temperature, pH, and the presence of competing ions or molecules in the effluent.
Regeneration and Reuse
One of the advantages of activated carbon adsorption is the potential for regeneration and reuse. Once the activated carbon becomes saturated with adsorbed dye molecules, it can be regenerated through thermal or chemical processes, allowing it to be reused for further adsorption cycles. This not only reduces the operational costs associated with frequent carbon replacement but also contributes to the overall sustainability of the treatment process.
Integration into Existing Treatment Systems
Activated carbon adsorption can be integrated into existing textile effluent treatment plants as a polishing step, complementing other treatment processes. In some cases, it may be employed as a primary treatment method, particularly for highly concentrated or recalcitrant dye streams. The versatility of this technology allows for customized solutions tailored to the specific requirements of each textile facility.
Conclusion
Using activated carbon in textile wastewater treatment plants is a big step in dealing with the problems caused by dye-filled wastewater. This method helps get rid of tough dyes and makes textile wastewater less harmful to the environment, which is good for sustainability.
As scientists keep working on this, we can expect activated carbon technology to get even better. It might be able to hold more dyes, target specific types of dyes better, and become easier to use again and again. Also, there's potential to use cheaper and more renewable materials to make activated carbon, which could make it more affordable for everyone.
Overall, using activated carbon in textile wastewater treatment isn't just about being good to the environment. It's also a smart move for the long-term health of the textile industry. By using this technology, textile makers can show they care about the environment, follow strict rules, and help make the world cleaner and greener for everyone.
Do you need an advice or assistance on selecting the best water and waste water treatment unit? We have solutions for all your problems!
Let us now your problem, our experts will make sure that it goes away.
For an assistance or related query,
Call on +91-965-060-8473
Or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com