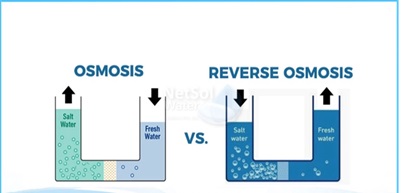
Osmosis and reverse osmosis differ primarily in that osmosis involves the diffusion of water molecules, across a semipermeable membrane from a high to a lower water potential, whereas reverse osmosis involves the diffusion of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane, against the potential gradient. Also, reverse osmosis is an artificial process, whereas osmosis is a natural process.
Let’s understand the difference between osmosis and reverse osmosis with examples in this blog.
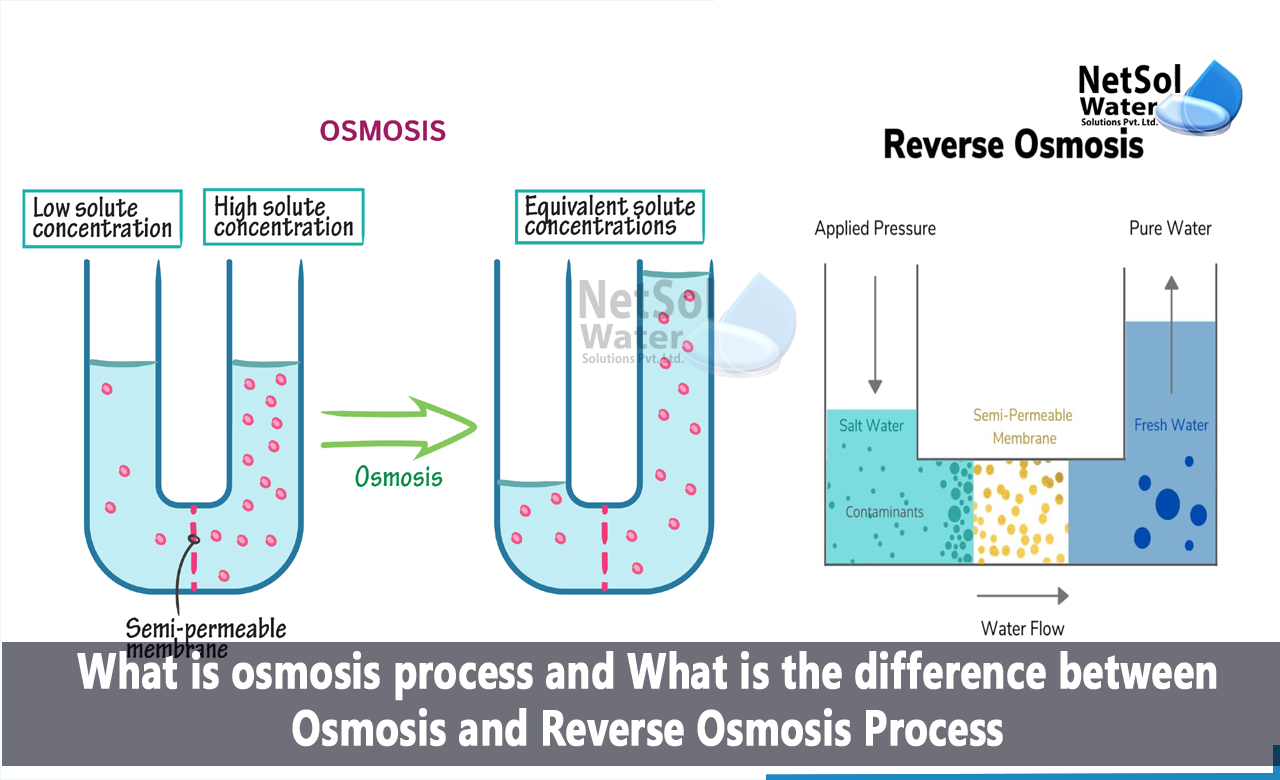
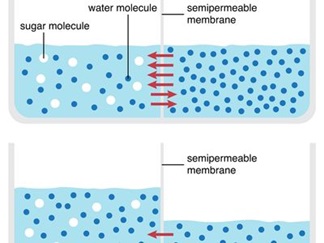
What is Osmosis?
It happens through a semipermeable membrane, primarily the cell's plasma membrane. Once the water potential on either side of the semipermeable membrane is equal, water molecules shift from a higher to a lower water potential. Endosmosis and exosmosis are the two primary types of osmosis that can take place within a cell.
Endosmosis: When cells are placed in a hypotonic solution, which has a higher water potential than the cytosol, endosmosis happens. Overfilling with water can occasionally cause cells to burst open.
Exosmosis: When cells are placed in a hypertonic solution, which has a lower water potential than the cytosol, exosmosis happens.
Examples of Osmosis
· Effects of introducing freshwater and saltwater fish to water with varying salt concentrations
· The plants are able to take in water from the soil via the osmosis process. Water seeps into the plant's roots, because they have a higher concentration of solutes, than the soil around them.
· Osmosis also affects guard cells in plants. These are cells that open and close on the underside of leaves to permit gas exchange. The guard cells swell and open the stomata, tiny openings that enable the plant to absorb carbon dioxide, when the plant's cells are full of water.
What is Reverse osmosis?
It is accomplished by raising the pressure on the side that is concentrated or has a lower water potential. This will shift water molecules to the side with the high water potential while keeping the majority of the salts in the concentrated side. As a result, the system's natural osmotic pressure is defeated by the applied pressure.
Contaminants removed from water by Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis purges feed water of 99% of dissolved salt particles, colloids, microorganisms, etc. The RO membrane separates the pollutants based on their size and charge. The likelihood that a contaminant will flow through the RO membrane increases with pollutant charge.
Application of reverse osmosis
The applications of reverse osmosis are as follows:
Desalinated water is created by water purification systems (RO Plants) using water from natural sources, which contains pollutants. The semipermeable RO membrane prevents these pollutants from passing through. Reverse osmosis can therefore be used to produce demineralized, desalinated, or deionized water, as well as recycling wastewater.

What is the difference between osmosis process and reverse osmosis process?
The difference between osmosis & reverse osmosis are in tabular form given below:
|
Osmosis |
Reverse Osmosis |
|
1) It is a process in which molecules of water of a solvent, pass through a semi-permeable membrane from a less concentred solution to the more concentred solution. |
It is a process in which molecules of water of a solvent, pass through a semipermeable membrane, in the opposite direction to that of natural osmosis, with hydrostatic pressure greater than osmosis pressure. |
|
2) It is a natural process. |
It is an artificial process. |
|
3) Osmosis occurs through a potential gradient. |
It needs energy to supply pressure. |
|
4) Osmosis occurs through a potential gradient passively. |
Reverse osmosis occurs against the potential gradient, with consumption of energy. |
|
5) Osmosis occurs from high water concentrations, to low water concentrations. |
The direction is opposite to that of osmosis. It occurs against the concentration gradient. |
|
6) Examples include:
Plant roots absorb water from the soil, water movement in and out all cells, etc. |
Examples include:
The process of reverse osmosis used in water purification, brewing of beer, hospitals, dental clinics, manufacturing industries, sterilization and in a clinical analysis, etc. |
Conclusion
There are two ways to transfer water across a semipermeable membrane: osmosis and reverse osmosis. But, reverse osmosis is the process of forcing excess pressure on the solution side of a semipermeable membrane, to transport a solvent from the solution to the pure solvent. It has wide application now-a-days to treat water and wastewater from a wide variety of industries.
Leading manufacturer of Commercial RO Plants in India
Netsol Water is the leading manufacturer, supplier, and exporter of a quality selection of Commercial RO plants in India. We provide a dependable and straightforward selection of customised RO plants. These Commercial RO Plants are one of the most sought- options on the market, since they are user-friendly and eco-friendly.
They are made with capacities ranging from 100 LPH to 10,000 LPH and even more to meet the most exacting requirements. According to individual needs, well-designed pretreatment and PLC/Controller-based automation are carried out.
Call us at +91 9650608473 or email at enquiry@netsolwater.com for further information.