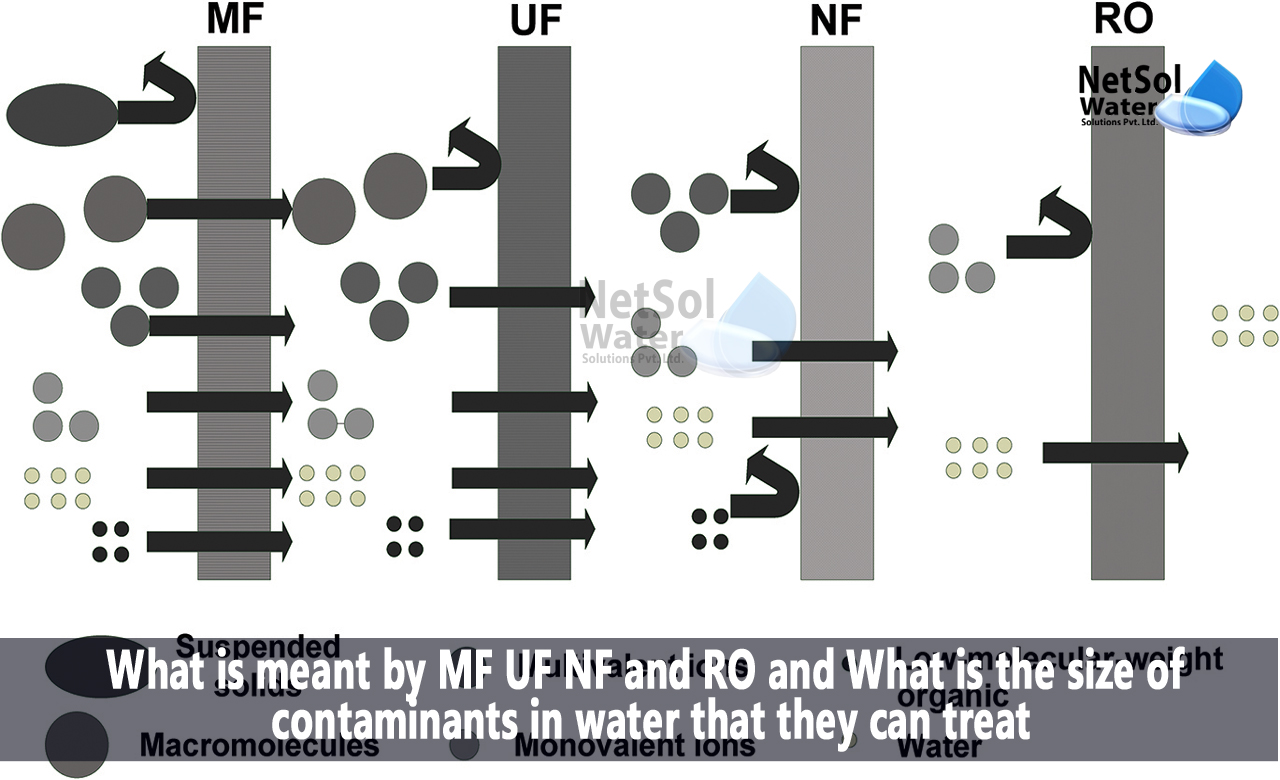
What is meant by MF UF NF and RO?
Membrane processes are the particle diffusion processes in water or wastewater. They work because specific membrane types permit the passage of particles with specific qualities, while preventing the passage of particles without those particular characteristics.
In this blog, we will discuss some of the membrane processes including microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration and reverse osmosis. We will also discuss about the size of the particle that these membrane processes can treat.
What are membranes?
Membranes are barriers used in water or wastewater treatment that let water pass through, while preventing undesired substances. These membranes filter out salts, pollutants, viruses, and other particles from water.
What is a membrane process?
Any technique that uses a membrane barrier to filter or remove particles from water, is referred to as a membrane process. The pressure difference between the membrane's two sides allows fluid, to move through the membrane. On one side, the contaminants persist.
The ability of membranes to separate tiny components like salts and ions from a liquid, sets them apart from other types of filtering media, such as clay, silt, and sand, which are all used to clean water.
What are the various types of membranes?
Depending on the impurities that need to be eliminated and the desired water quality by the end user, various types of membranes can be employed to treat water. Following are some of the processes:
|
Parameter |
Force |
Membrane process type |
|
Size |
Pressure |
Microfiltration |
|
|
|
Ultrafiltration |
|
|
|
Nano-filtration |
|
Size or Diffusion |
Pressure / Concentration |
Reverse Osmosis |
|
Ion Charge / Diffusion |
Electric field |
Electrodialysis |
|
Temperature |
Steam pressure |
Membrane distillation or MD |
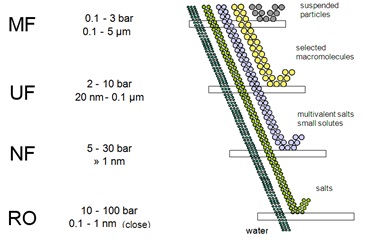
What is meant by microfiltration? What is pore size of a microfiltration (MF) membrane?
All forms of germs, turbidity, macromolecules, colloidal particles, etc. can be held in check, by micro-filtration membranes because of their 0.1–10 m pore size. These are used for water microbe reduction, cold sterilisation of liquid pharmaceutical and food, water pretreatment for nanofiltration and reverse osmosis, etc.
What is meant by ultrafiltration? What is pore size of an ultrafiltration (UF) membrane?
Particles of a size of 0.001-0.1 m are removed using ultra-filtration membranes. These membranes act as barriers to all viruses, macro-proteins, antibiotics, and other substances. These are used in the textile business, the treatment of wastewater, the removal of trihalomethanes from water, and the removal of dangerous organic compounds from the food and beverage industries.
What is meant by nanofiltration? What is pore size of a nanofiltration (NF) membrane?
Low molecular weight particles are partially held in the membrane by particles with a size of 0.1 nm to 0.001 m, facilitating water separation from the majority of molecules. Water softening, wastewater heavy metal removal, wastewater decontamination, reverse osmosis pretreatment, nitrate removal, colour removal, etc. all employ nanofiltration.
What is meant by reverse osmosis? What is the pore size of RO membranes?
When two dilutions are placed one on either side of a semipermeable membrane, the chemical potentials of the two dilutions tend to equalize, causing reverse osmosis to occur.
It works by pumping water that has been charged with dissolved ions into a tank, and pressing it up against a membrane. Water is moved from one side of the membrane to the other during this procedure.
To avoid an increase in ion concentration that could cause salts to precipitate on the membrane surface, the concentrate produced should be removed from direct contact with the membrane. As a result, the process becomes less effective and requires more maintenance, which raises expenses. Pretreatment must be carried out in order to avoid blockage.
The pore size of a reverse osmosis filter is about 0.0001 micron. Reverse osmosis systems are particularly successful at getting rid of bacteria like Campylobacter, Salmonella, Shigella, and E. coli. They are also very effective at getting rid of protozoa like Cryptosporidium and Giardia. They are used in the treatment of water, wastewater, seawater desalination, wastewater recycling, etc.
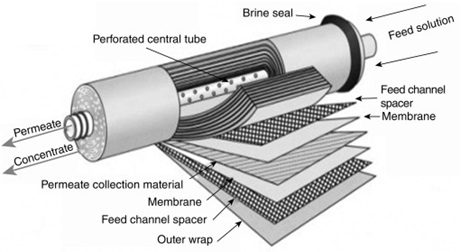
Diagrammatic representation of various types of Membrane processes
Conclusion
Thus, we can conclude that the membranes for reverse osmosis is generally used in the separation of suspended materials, membranes for nanofiltration are used in concentration processes and wastewater treatment, ultrafiltration membranes are used in the oil separation processes, and by using microfiltration membranes, a liquid phase can be separated from its largest particles.
Pressure, temperature, vibration amplitude, and the length of time the substance is present inside the membrane, are crucial variables for efficient membrane processes.
Get in touch with us to get high-quality water treatment!
Contaminated water is harmful to the environment and to people's health. To prevent water pollution and to provide safe and clean drinking water to people, poisonous and dangerous substances that are released into the water must be eliminated.
In this regards, Netsol Water provides various water treatment solutions for any sector with high-quality, dependable products and a knowledgeable engineering group, such as Commercial RO Plants, Industrial RO Plants, Water Softeners, DM Plants, EDI plants, etc. To find out more about our alternatives for treating water, get in touch with us. Call us at +91 9650608473 or email at enquiry@netsolwater.com for further information.