Overview
Human activities generate a wide range of by-products. Organic and inorganic residual chemicals are left behind by agriculture, mining, manufacturing, and other industrial operations. Some are safe and inert, while many are toxic and extremely harmful to the environment, especially the soil and groundwater. Our planet, fortunately, has built-in environmental clean-up processes. Natural groundwater and soil clean-up, unfortunately, takes a long period.
For restoring damaged soil and water, bioremediation technology is invaluable. Bioremediation, in its most basic form, is a waste management procedure that employs live organisms to neutralise or eliminate hazardous chemicals from contaminated areas.
What is bio remediation?
Bioremediation is a branch of environmental science that enhances natural biological processes in order to treat or remediate a poisoned soil and polluted groundwater. Bioremediation approaches employ biological bacteria to undertake the clean-up work instead of expensive environmental remediation equipment to remove untreated harmful chemicals and dispose of them elsewhere.
Microbes are microscopic organisms that live in the environment. These bacterial microbes aid in the decomposition, recycling, and correction of chemical imbalances in soil and water. Nature has been correcting itself for thousands of years, while humans continue to demonstrate a remarkable ability to make a mess and ignore the consequences. However, by adding natural organic molecules and utilising their inherent qualities, research has discovered an effective technique to remediate poor soil and groundwater conditions.
Bioremediation is a water and soil treatment technology that uses naturally occurring organisms to attack hazardous pollutants and transform them into less toxic substances, according to the Environmental Protection Agency. Using correct bioremediation techniques and specialised equipment, extremely contaminated locations can often be made toxin-free.
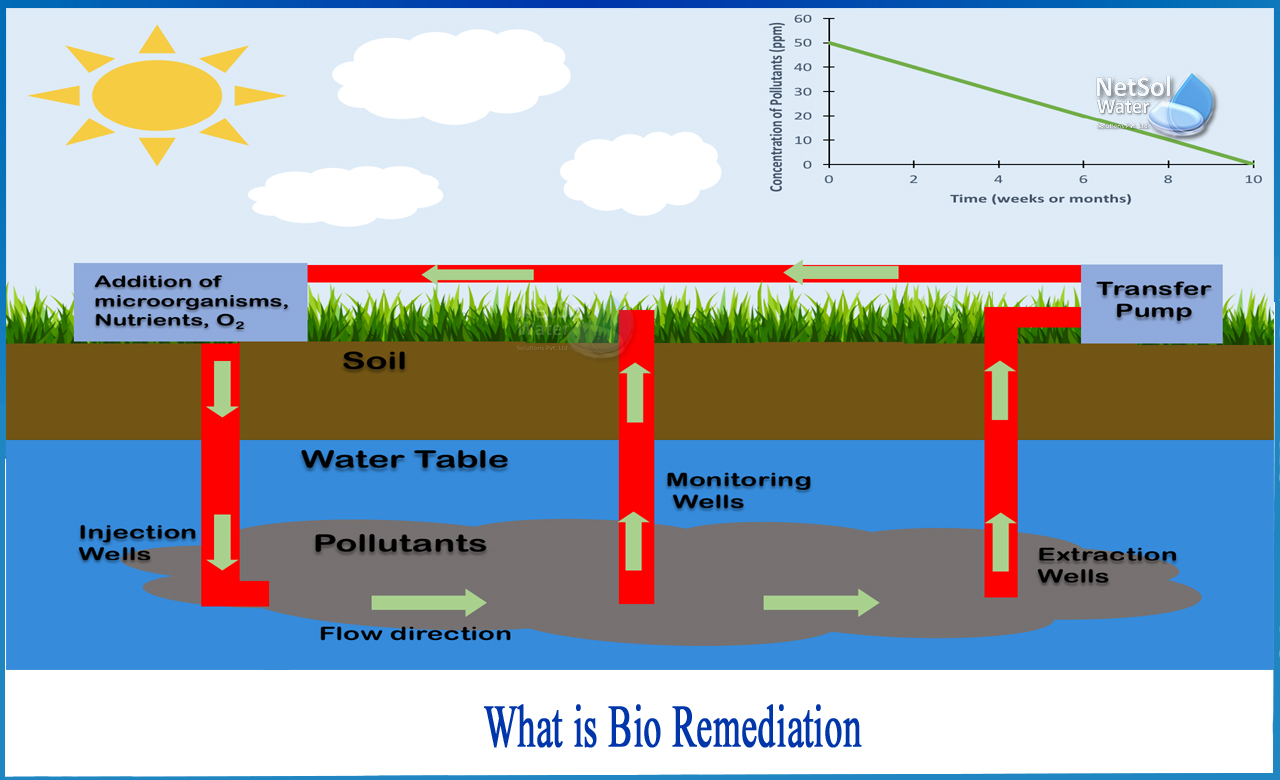
How does Bioremediation Work?
The bioremediation process is a biological process that encourages beneficial bacteria to feed and grow by consuming harmful toxins. Toxic chemicals and pathogens are consumed by microorganisms, which digest them and eliminate them by altering their composition into harmless gases such as ethane and carbon dioxide. The proper counter-microbes are already present in some contaminated soil and water environments. By enhancing microbial action, human intervention can speed up the natural restoration process.
Critical conditions for bioremediation are
- Host microbial contaminants that provide parasitical bacteria with fuel and energy
- Parasitic microorganisms that feed on and destroy their toxic hosts
- Adequate oxygen levels to support aerobic biodegradation
- Water, whether liquid or in the form of soil moisture content
- Carbon is the building block of microbial life and the source of its energy
- A temperature that is neither too cold nor too hot for microbiological life to thrive
- Microbe growth nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and sulphur
- Acid-alkaline proportions or pH ratios in the 6.5-7.5 range
Microbes proliferate at huge speeds when all of these variables are in the appropriate proportions. If the optimum conditions are out of balance, microbial action is slowed or stopped entirely, and pollutants persist until nature restores the equilibrium. In extremely contaminated environments, rebalancing might take a long period. However, proper bioremediation procedures may fix most problems in a short amount of time. That time span can range from a few years to several decades.
Bioremediation is greatly aided by the presence of oxygen!
Some microbes flourish in the presence of oxygen, whereas others are hampered by it. This effect is entirely dependent on the sort of toxin being remediated and the bacteria being promoted.
Oxygen levels in soil and water are divided into two groups or processes-
The presence of oxygen required for microbial development is referred to as aerobic. Tilling the soil on a regular basis is one way to improve aerobic conditions in polluted soil. This approach is also used to oxygenate beneficial fungus in composting. Aerobic action can also be induced mechanically through passive bioventing or biosparging, which involves pumping compressed air into the soil or beneath the water table.
The lack or diminution of oxygen in water or soil is referred to be anaerobic. Except under heavy metal situations, such as mitigating areas polluted by polychlorinated biphenyls or trichloroethylene, this type of bioremediation is unusual. Anaerobic remediation is a highly specialised process that necessitates advanced technology and meticulous monitoring.
Conclusion
It's widely utilised around the world in a variety of scenarios where previous human activity has harmed and rendered a site unsuitable without repair. As the country's population rises, there are fewer landfills accessible to dispose of toxic waste. This is why bioremediation is so appealing. Bioremediation is also cost-effective, thanks to advances in science.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.