Biodiversity typically enhances the beauty, maintains the planet's equilibrium, and aids in its proper functioning. It specifically refers to the diversity of life on Earth. Given the variety of biodiversity, it is possible that the greatest value of biodiversity is still undiscovered. Even before we realise what is lost, a large portion of the biodiversity on Earth is vanishing at an alarming rate. But, experts and researchers from all over the world are attempting to identify the real cause, and stop or reduce the rate of loss.
Here, we go over the meaning of biodiversity, various forms of biodiversity and its specifics. Also, let's first take a moment to define biodiversity and grasp its significance and importance.
What do you mean by biodiversity in environment?
Biodiversity is the term used to describe the variety of all life forms on the Earth, including the different species of animals, plants, and microorganisms, as well as the terrestrial, marine, and freshwater ecosystems to which they contribute.
Biodiversity is dynamic and ever-evolving. It is boosted by genetic evolution and other processes, and it is diminished by others including habitat destruction, population decrease, and extinction.
What is the value of biodiversity?
Every ecosystem needs biodiversity because it is essential to, ecosystem function and services. Many sorts of diversity contribute to preserving the harmony of nature. Hence, it follows that maintaining biodiversity is crucial to keeping life on Earth alive.
Importance of biodiversity
The following a?re some of the fundamental causes for why biodiversity is important:
· Environmental Stability
Each species contributes significantly to an environment. Typically, they seize and hold the energy needed for biological processes. Throughout the environment, they also create and break down organic molecules. Many services provided by the ecosystem are essential for human survival. Also, there is a connection between various species and the ecosystem services.
Consequently, a diverse, productive ecosystem results in ecological stability and aids ecosystems in withstanding environmental pressures.
· Financial importance
Biodiversity is a rich source of materials for making medicines, food, cosmetics, and other goods. Crops, animals, fisheries, and forests are some examples of abundant food resources.
Several wild plants, like Cinchona can be utilised as medicines, and are important supplies for pharmacies. The majority of resources, including wood, fibre, lubricants, resins, come from different plant species.
· Ethical value
Everyone has the right to survive since every species has a place in the ecosystem. People should not cause them troubles, and should instead assist them in surviving.
The right of humans to contribute to the extinction of any species is inalienable. Moreover, biodiversity preserves the existence of various civilizations and spiritual traditions, and aids in maintaining the equilibrium between various species. Consequently, biodiversity conservation is crucial.
· Diversity of the life on land as well at sea
Significant threats to terrestrial biodiversity include habitat fragmentation and land clearing, etc.
Freshwater biodiversity is declining at far faster rates, and it is threatened by pollution, overuse of water resources, changes to water flows and hydrology, degradation of habitats, and invasive species.
The loss of coastal habitat, dredging and spoil disposal, marine pest invasion, sedimentation and pollution from industry and land-use practises, unsustainable fishing methods, and recreational activities, all have a negative influence on marine and estuarine biodiversity.
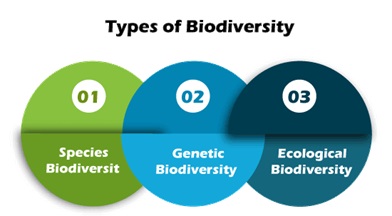
What are the different types of biodiversity?
The following three categories of biodiversity are essential:
1: Species Biodiversity
2: Genetics Biodiversity
3: Ecological Biodiversity
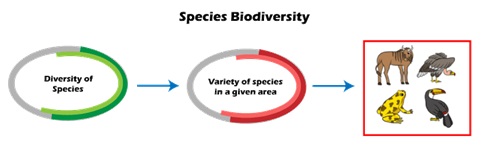
What is species diversity?
The term "species diversity" describes a collection of related organisms that normally reproduce through mating. They frequently come from the same family. The most fundamental classification unit is species diversity, which covers all species from different types of plants to different microbes.
Furthermore, despite belonging to the same species group, two different people are diverse and do not exactly resemble one another. For instance, no two people are exactly alike. Aside from this, there is a high degree of variation among individuals, living in different parts of the world.
There are almost 5–10 million species in the world, yet only 1.75 million of them have been given scientific names on Earth. There are more species in certain places than others. 'Biodiversity Hotspots' of diversity refer to regions with higher species diversity.
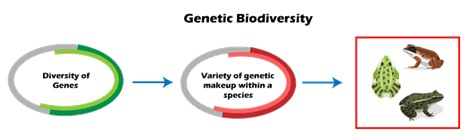
What is Genetic Diversity?
It alludes to variations in an organism's genetic resources. Each member of a specific species differs from the others, in terms of genetic makeup. Because of this, every individual is unique. That is why, there are various kinds of the species of rice, wheat, maize, barley, etc.
Because, there are numerous gene combinations that can result in an individual having a certain set of traits, every member of every species of animal or plant is genetically distinct from the others, in a significant way. The healthy reproduction of a species depends on this genetic diversity.
In order to develop new varieties of more productive crops and breed better domestic animals, the diversity of nature is now more actively exploited. Genes are manipulated by modern biotechnology to create a wide range of substances and improved medicine types. Despite the fact that all species share a single or common ancestor, species diverge and develop new distinctive traits over time, which adds to biodiversity.
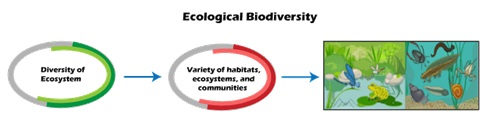
What is Ecological Diversity?
The intricate web of many species found in nearby habitats and their dynamic interactions is known as ecological variety. An ecosystem is made up of several species of living things connected through the movement of matter, energy, and nutrients across the area. These interactions between creatures of various species result in those partnerships.
We also know that the plants transform the sun's radioactive energy into chemical energy. When animals eat plants and are then consumed by other species, this energy is released from those systems. Fungi obtain their energy from decaying organisms, which provide nutrients to the soil. As a result, an ecosystem consists of both living and non-living elements that are linked by energy flow and interact with one another, including microorganisms, plants, animals, and fungus.
Types of Ecological biodiversity
Ecological biodiversity is related to the coexistence of different plant and animal species, connected through the food web and food chain. Ecological diversity is a component of diversity in a variety of habitats, such as deserts, rain forests, mangroves, etc. In a region, it is typically seen between various ecosystems.
The diversity of various species in a landscape is often measured on three different scales, giving rise to ecological diversity's three main perspectives.
· Alpha Diversity
The sort of ecological diversity found inside a particular area, community, or ecosystem is known as alpha diversity. Alpha diversity is more particularly the species diversity that exists within a community on a local or small scale, typically the size of a single ecosystem. It is typically portrayed by the total number of distinct species (or species richness) in that specific area.
The total number of taxa (different biological groups) within the associated environment, is a common indicator of this (species, genera, and families). In particular, when we consider diversity in a field, we frequently think about alpha diversity.
· Beta Diversity
Beta diversity is a category of ecological diversity that is determined by comparing the species variety, inside and across various ecosystems, as well as along with environmental gradients. Beta diversity is often measured by comparing the counts of species that are specific to each habitat.
Therefore, it can be described as the measurement of species variety between two distinct entities at a wider scale, typically separated by a particular geographical barrier like a mountain range or river. It is the rate at which species composition varies between communities or across habitats. The diversity of communities that are affected by changing surroundings is also quantified by beta diversity.
· Gamma Diversity
Gamma diversity is frequently used to describe the abundance of all species over a wide area. It is a measurement of an area's overall diversity across all different types of ecosystems.
Simply put, it is frequently researched as a biome where the species variety between various habitats is examined.
Biodiversity in India
India is one of the world's most diversified countries. In terms of the diversity of plant species, it comes in tenth. India is home to two of the top 25 biodiversity hotspots on earth. Important agricultural species like the pigeon pea, eggplant, cucumber, cotton, and sesame are descended from it. Many domesticated species, including millets, grains, legumes, vegetables, medicinal and aromatic crops, etc., are also widely grown in India.
India's wealth in fauna is also very diverse. About 91,000 different animal species can be found here. Many programmes on biodiversity conservation are being implemented to preserve nature, yet diversity is disappearing at a rapid rate.
Now, with all the knowledge of biodiversity conservation, we as an individual must take steps to protect our air, water, land as well as the living species. As responsible citizens of India, and environment lovers, we at Netsol Water take pledge to protect our biodiversity, save water and treat wastewater.
Netsol Water is the leading manufacturer, supplier, and exporter of a quality selection of water treatment plants, and wastewater treatment plants in India.
We provide various capacities of Industrial and Commercial RO Plants, water softeners, ETPs, DM plants, Ultra filtration plants, UV water purification systems, STPs, ZLD plants, and other goods and services. We also provide water and wastewater treatment solutions to businesses including pulp & paper, automotive, beverages, textile, pharmaceutical, refineries, hotels, schools, office buildings, hospitals, among others.
Call us at +91 9650608473 or email at enquiry@netsolwater.com for further information.