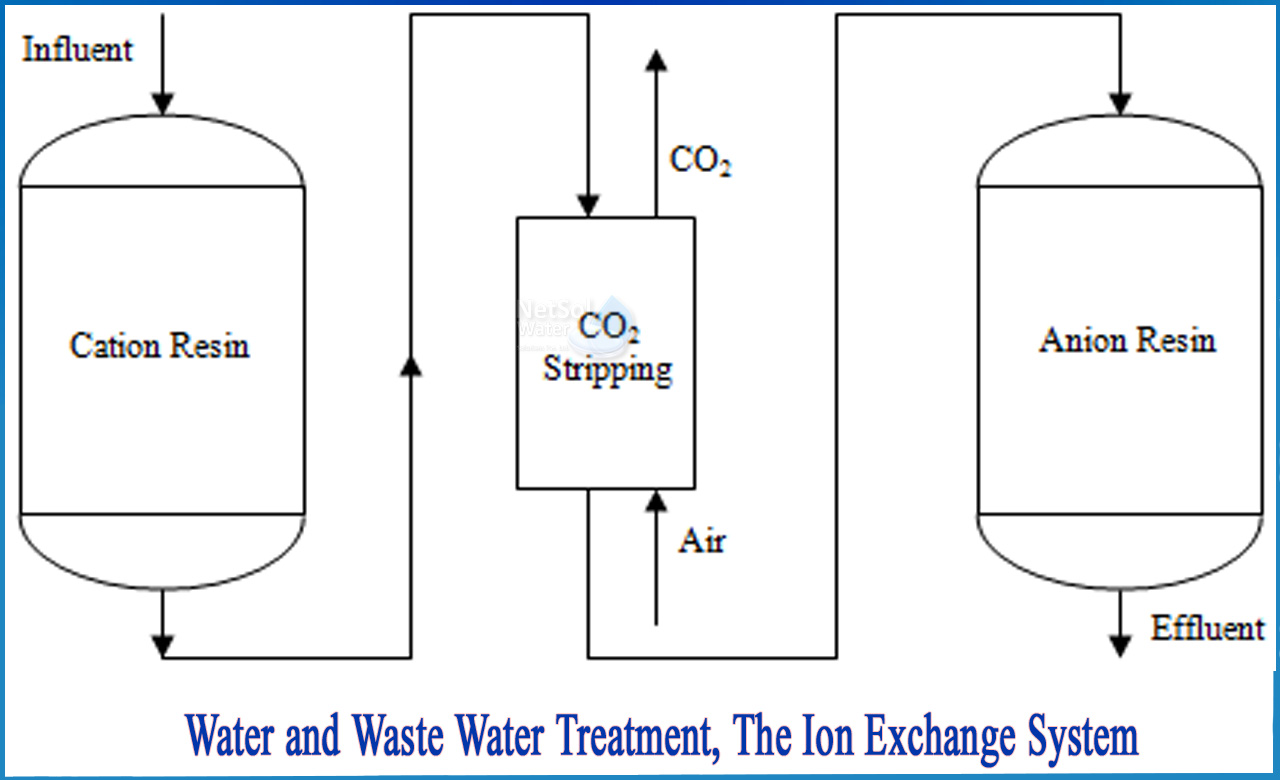
How do work Ion exchange system for water and waste water treatment?
Ion exchange is a water treatment method that involves exchanging one or more undesirable ionic contaminants for another non-objectionable or less objectionable ionic substance. The contaminant and the exchanged substance must both be dissolved and have the same electrical charge type (positive or negative). Ion exchange is commonly used in the process of "water softening," which aims to reduce calcium and magnesium content. Despite this, ion exchange is effective at removing toxic metals from water.
Water softening is simply the process of removing the minerals that cause water hardness, such as calcium and magnesium, from water. Softened water is ideal for most industrial, commercial, and residential applications because it reduces scaling and does not limit the use of soap cleaners.
The use of hardened water causes soap waste and the formation of hard scales on equipment due to the reaction of magnesium and calcium ions with fatty acids. The primary water softening mechanisms are ion exchange and the use of chemicals like sodium carbonate and slaked lime.
Ion exchangers can be unselective or have binding preferences for specific ions or classes of ions, depending on their chemical structure. This can be determined by the ion's size, charge, or structure. Ions that can commonly bind to ion exchangers include:
- H+ is proton and OH- is hydroxide
- Single charged monoatomic ions like Na+, K+, or Cl-
- Double charged monoatomic ions like Ca2+ or Mg2+
- Polyatomic inorganic ions like SO42- or PO43-
- Organic bases, usually molecules containing the amino functional group -NR2H+
- Organic acids, often molecules containing -COO- (carboxylic acid) functional groups
- Biomolecules which can be ionized: amino acids, peptides, proteins, etc.
Ion exchange is a reversible method, and the ion exchanger can be regenerated or loaded with desirable ions by washing with a large amount of these ions.In the chemical industry, ion exchangers are also used to remove or recover metal ions from wastewater. Because of the low selectivity of the resins, some contaminants (such as arsenic, fluoride, and lithium ions) are difficult to remove using ion exchange.
The ion-exchange process is also used to separate other sets of chemical elements that are very similar, such as zirconium and hafnium, which are also very important in the nuclear industry. Although zirconium is practically transparent to free neutrons and is used in reactor construction, hafnium is a very strong neutron absorber and is used in reactor control rods.
Ion exchangers are being used in nuclear reprocessing and radioactive waste treatment. Thin membrane ion exchange resins are used in the chloro-alkali process, fuel cells, and vanadium redox batteries. Ion exchange can also be used to eliminate hardness from water by exchanging calcium and magnesium ions in an ion exchange column for hydrogen and chlorine ions.
COSTS OF ION EXCHANGE SYSTEM
The costs of ion exchange systems vary greatly depending on scale and location. Furthermore, costs are determined by pre-treatment requirements, discharge requirements, and utilisation. Water softening equipment maintenance varies depending on the type of softener. In most cases, some level of monitoring or management of the regeneration process is required. Adequate backwashing of the resin bed is required to ensure the unit's regeneration. However, regeneration generates waste.
HOW ION EXCHANGE IS HEALTHY?
People on sodium-restricted diets for medical reasons should account for increased intake through softened water. It is common practise to avoid drinking and cooking with softened water by installing a cold water line to the kitchen faucet that bypasses the water softener. This produces hard water that can be used for drinking, cooking, and other purposes. Because of the sodium content, it is not recommended to use softened water on plants, lawns, or gardens on a regular basis.
ADVANTAGES OF ION EXCHANGE
1. One of the most effective technologies for removing dissolved inorganic ions
2. Possibility of resin regeneration
3. Initial capital investment is relatively low.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.