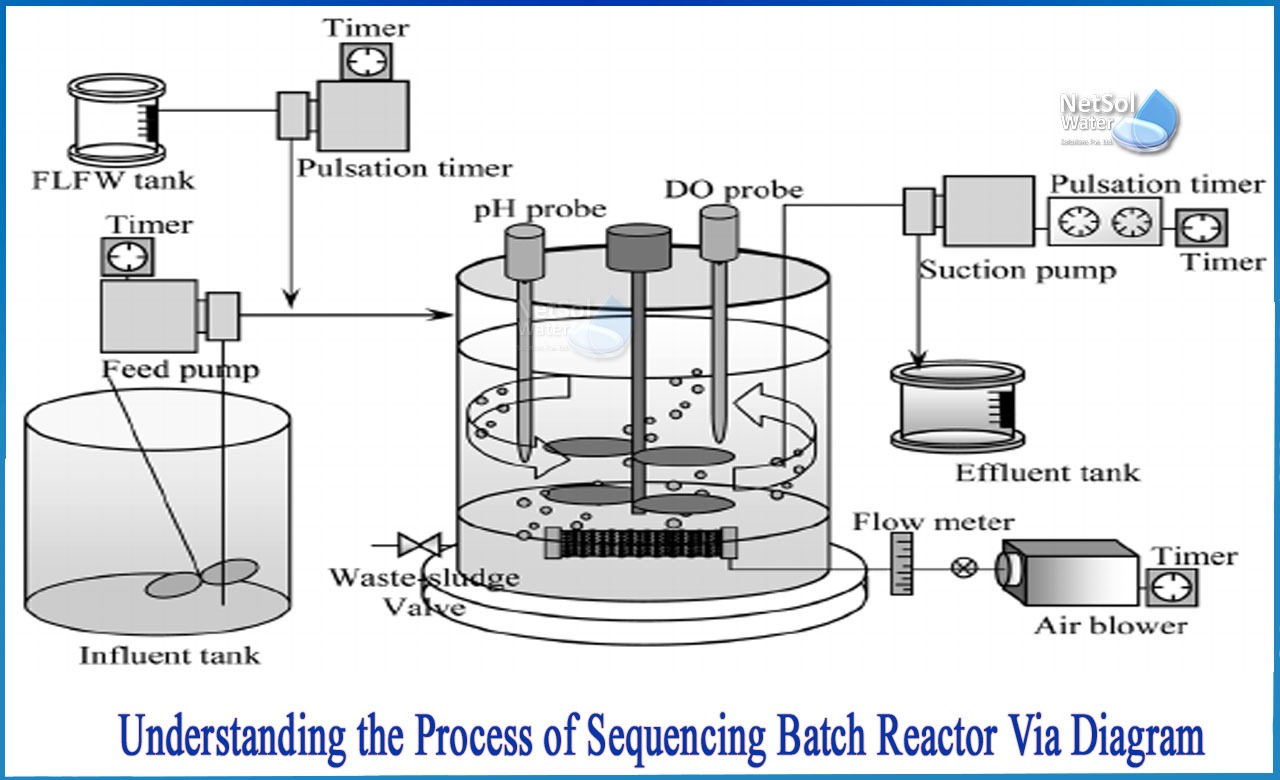
What is Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR)?
The sequencing batch reactor (SBR) is a wastewater treatment technology that uses a fill-and-draw activated sludge technique. In this system, wastewater is pumped into a single "batch" reactor, where it is treated to eliminate contaminants before being discharged. A single batch reactor can be used for equalization, aeration, and clarifying. Two or more batch reactors are employed in a predetermined sequence of operations to improve the system's performance. Both municipal and industrial wastewater have been effectively treated using SBR systems. They're especially well-suited to wastewater treatment applications with low or intermittent flow rates.
Fill-and-draw batch operations, similar to the SBR, are not as new as many people believe. Several full-scale fill-and-draw systems were in use between 1914 and 1920. With the advent of new equipment and technology in the late 1950s and early 1960s, interest in SBRs was reignited. SBRs have been able to compete successfully with traditional activated sludge systems, thanks to advancements in aeration devices and controls.
Process description:
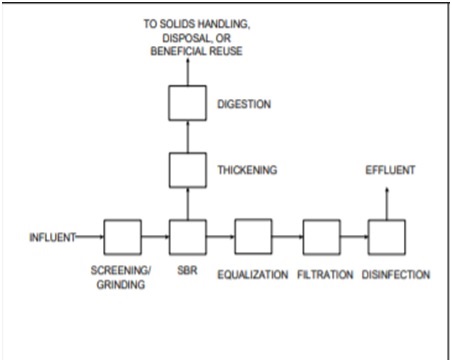
Figure depicts a typical process flow diagram for a municipal wastewater treatment plant employing an SBR.
Working of SBR:
Prior to the SBR, most influent wastewater travels via filters and grit removal. The wastewater is then pumped into a partially filled reactor with biomass that has been acclimated to the wastewater contents during previous cycles. When the reactor is full, it functions like a traditional activated sludge system, but without the constant flow of influent or effluent.
After the biological reactions are complete, the biomass settles, and the treated supernatant is removed, the aeration and mixing are turned off. At any point during the cycle, excess biomass is squandered. The mass ratio of influent substrate to biomass is essentially constant from cycle to cycle due to frequent waste. As influent flowrates, characteristics, and settling tank underflow concentrations change, continuous flow systems modify return activated sludge flowrates to maintain the mass ratio of influent substrate to biomass.
Following the SBR, the wastewater "batch" may flow through an equalization basin, where the wastewater flowrate to additional units processed can be controlled at a set rate. In some circumstances, the wastewater is filtered and disinfected after it has been filtered to eliminate any remaining solids.
The solids handling system could include a thickening and an aerobic digester, as shown in Figure. Return activated sludge (RAS) and primary sludge (PS) pumps, which are used in traditional activated sludge systems, are not required with SBRs. There is usually only one sludge to deal with while using the SBR.The use of gravity thickeners before digestion is selected on a case-by-case basis based on the sludge's characteristics.
When the vessel is filled with wastewater, an SBR acts as an equalization basin, allowing the system to tolerate peak flows or peak loads in the influent and equalize them in the batch reactor. Separate equalization is required in many traditional activated sludge systems to protect the biological system from peak flows that could wash out the biomass or peak loads that could disrupt the treatment process.
It's also worth noting that primary clarifiers aren't usually needed before an SBR in municipal wastewater applications.
Prior to the biological system, primary clarifiers are employed in most traditional activated sludge wastewater treatment plants. If the total suspended solids (TSS) or biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) are larger than 400 to 500 mg/L, the SBR manufacturer may prescribe primary clarifiers.
To assess whether primary clarifiers or equalization are recommended prior to an SBR for municipal and industrial uses, historical data should be analyzed and the SBR manufacturer consulted. Depending on the downstream procedure, equalization may be required after the SBR. If equalization is not employed before filtering, the filters must be sized to receive the batch of effluent from the SBR, resulting in a large filtration surface area. Equalization is employed between an SBR and downstream filtering because sizing filters to take these batch flows is usually not possible.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.