What are The process of Electrocoagulation in STP?
Water is one of human being's most fundamental needs.
Globalization, uncontrolled growth, and other causes are causing a lack of fresh water, and many countries are concerned about the problem. As a result, it's critical to consider water purifying processes that are both effective and affordable, as well as reusability. People are presently aware of a wide range of wastewater treatment options. With recent technological advancements in the electrochemical area, a new technique known as electrocoagulation has been introduced into the business.
Here major goal is to focus on electrocoagulation process technique and applications!
Introduction of the process
Filtration, air stripping, ion exchange, chemical precipitation, chemical oxidation, carbon adsorption, ultrafiltration, reverse osmosis, electrodialysis, volatilization, and gas stripping are the traditional physico-chemical treatment techniques utilized for wastewater treatment.
The electrocoagulation process is a sophisticated electrochemical technology-based procedure. Electrocoagulation (EC), which involves sending an electric current through water to remove pollutants, has shown to be quite successful. Anode and cathode geometries such as plates, balls, fluidized bed spheres, wire mesh, rods, and tubes have been used in electrocoagulation systems for many years.
Water containing foodstuff wastes, oil wastes, dyes, suspended particles, chemical and mechanical polishing waste, organic matter from landfill leachates, de-fluorination of water, synthetic detergent effluents, mine wastes, and heavy metal-containing solution have all been treated with it in recent decades. By decreasing electricity usage and miniaturizing the required power supply, EC has become one of the most cost-effective wastewater treatment systems in the world.
Parameters removed by EC
EC removes metals, colloidal solids and particles, and soluble inorganic contaminants. EC treats a wide spectrum of waste streams comprising heavy metals, virus, bacteria, pesticides, arsenic, MTBE, cyanide, Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), Total dissolved solids (TDS), and Total suspended solids (TSS) using a specialized treatment chamber and electricity. It is used to treat wastewater from municipal, industrial, and commercial sources.
Methodology involved
For breaking stable emulsions and suspensions, EC is a viable alternative to metal salts, polymers, and polyelectrolyte addition.
An electrolytic cell with one anode and one cathode makes up an EC reactor. The EC system is made up of two parallel pairs of conductive metal plates that operate as monopolar electrodes.
The criteria for using EC are as follows:
· A power source that uses direct current
· Box of Resistance
· Multimeter
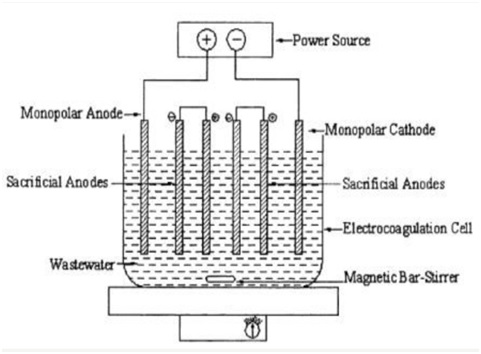
Fig: Bench-scale EC reactor with monopolar electrodes in series connection
1: "Sacrificial electrodes" is a term used to describe the conductive metal plates. The sacrificial anode decreases the anode's dissolving potential and reduces the cathode's passivation. The materials used for the sacrificial anodes and cathodes might be the same or different.
2: The cells are connected to monopolar electrodes in a series. Because the cells connected in series have higher resistance, a bigger potential difference is required for a given current to flow in a series cell configuration. During electrolysis, anodic reactions occur on the positive side, whereas cathodic reactions occur on the negative side. The coagulation process will begin with released ions neutralizing the charges of the particles.
3: The released ions eliminate undesired impurities by forcing colloidal materials to agglomerate, which can then be removed by flotation. When water containing colloidal particles, oils, or other pollutants passes through an electric field, ionization, electrolysis, hydrolysis, and the generation of free radicals can occur, altering the physical and chemical characteristics of the water and contaminants. Contaminants are liberated from the water and destroyed or rendered less soluble due to the reactive and excited condition.
Conclusion
Electrocoagulation is capable of treating wide range of wastewaters. It is the technique of using a little amount of electrical current to destabilize suspended, emulsified, or dissolved pollutants in an aqueous media. As a result, the process's extra expenses are reduced.
When it comes to the advantages, the EC method aids in the elimination of TSS by 95-99%, BOD by 50-99%, and bacteria by 95-99%. This shows that the technology is successful and dependable for a wide range of future uses, providing hope for everyone to have access to clean water.
How can you use modern technology to improve your industries water efficiency?
Contact specialists from Netsol Water to learn how recent technology can be adopted for wastewater reuse and waste-to-energy. Desalination and other membrane (RO)
technologies as well as electrocoagulation might help you prepare for a future that is increasingly water-stressed.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.



