- For Enquiry- 0120-2350053 || +91 9650608473 || +91 9650795306
- enquiry@netsolwater.com



Human beings transitioned from hunting to farming resulting in the Agrarian revolution. The first industrial revolution (1.0) began in the mid of the 18th century. This was triggered by the invention of the steam engines, railroads, and mechanical production. The second industrial revolution begins in the late 19th century which was triggered by the invention of electricity and assembly line production in the early 20th century. The third industrial revolution (3.0) was triggered by the invention of the semiconductors followed by supercomputers, personal computing, and the internet by the end of the 20th century.
We are now living in one of the most exciting times that the world has ever seen. The advent of the fourth Industrial Revolution has taken the world by storm. The revolution has spread its tentacles to almost every function and every industry domain. The pace and scope of path-breaking scientific and technological advancements from Large Enterprises, Startups, Research Institutions, and Educational Institutions are mind-boggling.
Technology is rapidly changing the way humans are behaving, working, and engaging in the planet today. The technologies that are driving the Industry Revolution will fundamentally transform the world’s economic, social, and community aspects. We are at the beginning of a revolution that is fundamentally changing every aspect of the world through its speed, scope, scale, and complexity. We are witnessing a fusion of technologies across the physical, digital, and biological worlds.
Governments, businesses, academia, and civil societies have to work together in a systematic and well-coordinated way to ensure the best results. With the length and breadth of revolution, there will be profound shifts across all industries.
Digital technologies that have computer hardware, software, and networking as their core is becoming more sophisticated as well as integrated. These digital technologies will manifest through the force of full-fledged automation of almost every process.
Industry 4.0 will revolutionize the organization of global value chains. By enabling smart factories, smart cities, and smart homes the fourth industrial revolution creates a world in which virtual and physical systems of manufacturing globally cooperate with each other in a flexible way. This enables the complete customization of products to the required needs as well as the creation of new operating business and manufacturing models.
The fourth industrial revolution will go beyond smart and connected machines and systems. The breakthroughs in genetics, nanotechnology, renewable systems, quantum computing are spellbinding. What differentiates the industrial revolution 4.0 fundamentally from the earlier revolutions is the fusion of these advancing technologies and the cross-domain interaction across physical, biological, and digital worlds. This revolution has also witnessed the dispersion of emerging technologies and broad-based innovation at a much faster pace and a much broader scale when compared to the earlier revolutions.
The extent to which the society embraces technological innovation will be a major determinant of progress arising out of Industrial revolution 4.0. The government and public institutions, as well as the private sector, need to play an important role. But far important is for the citizens to see the long-term benefits of the industrial revolution.
The fourth industrial revolution will be farther powerful, impactful, resourceful, beneficial, disruptive, and historically important when compared to the previous three revolutions.
For the potential of the fourth industrial revolution to be effective and cohesively realized, we need to understand the limiting factors.
Firstly, the requisite levels of leadership as well as an understanding of the changes underway, across all sectors, are low when compared with the need to rethink and redesign political, social, economic systems to respond to the fourth industrial revolution. Consequently, both at the national as well as global levels, the requisite institutional framework to govern and administer the diffusion of innovation and mitigate the disruption is either inadequate at best or at worst absent altogether.
Secondly, the world lacks a positive and common narrative that focuses on the opportunities and challenges of the fourth industrial revolution, if we need empowerment and diversity, we need to avoid backlash against the fundamental changes
Major technological innovations are on the verge of precipitating momentous change throughout the different corners of the world.
The scale and scope of change is the reason for the acute disruptions and innovations of today. The speed of innovation in terms of both its development as well as diffusion is faster than ever before. Today’s disruptive technologies, solutions, systems, and companies were relatively unknown just a few years ago. But it is not only speed; returns to scale are equally staggering. Digitization means automation, which in turn means that companies do not incur diminishing returns to scale (or less of them).
A unit of wealth is created today with much fewer workers compared with that a decade ago. This is possible because digital businesses consist of marginal costs that tend towards zero. With the advent of the digital age, many new businesses provide “information goods” with storage, transportation, replication, and multiplication costs that are virtually nil. Some disruptive technology companies require lesser capital to prosper. These did not require much funding to start up, changing the role of capital, and scaling the business in the context of the fourth industrial revolution.
Companies are able to scale themselves faster with lesser capital, manpower, and through the use of advanced automated systems.
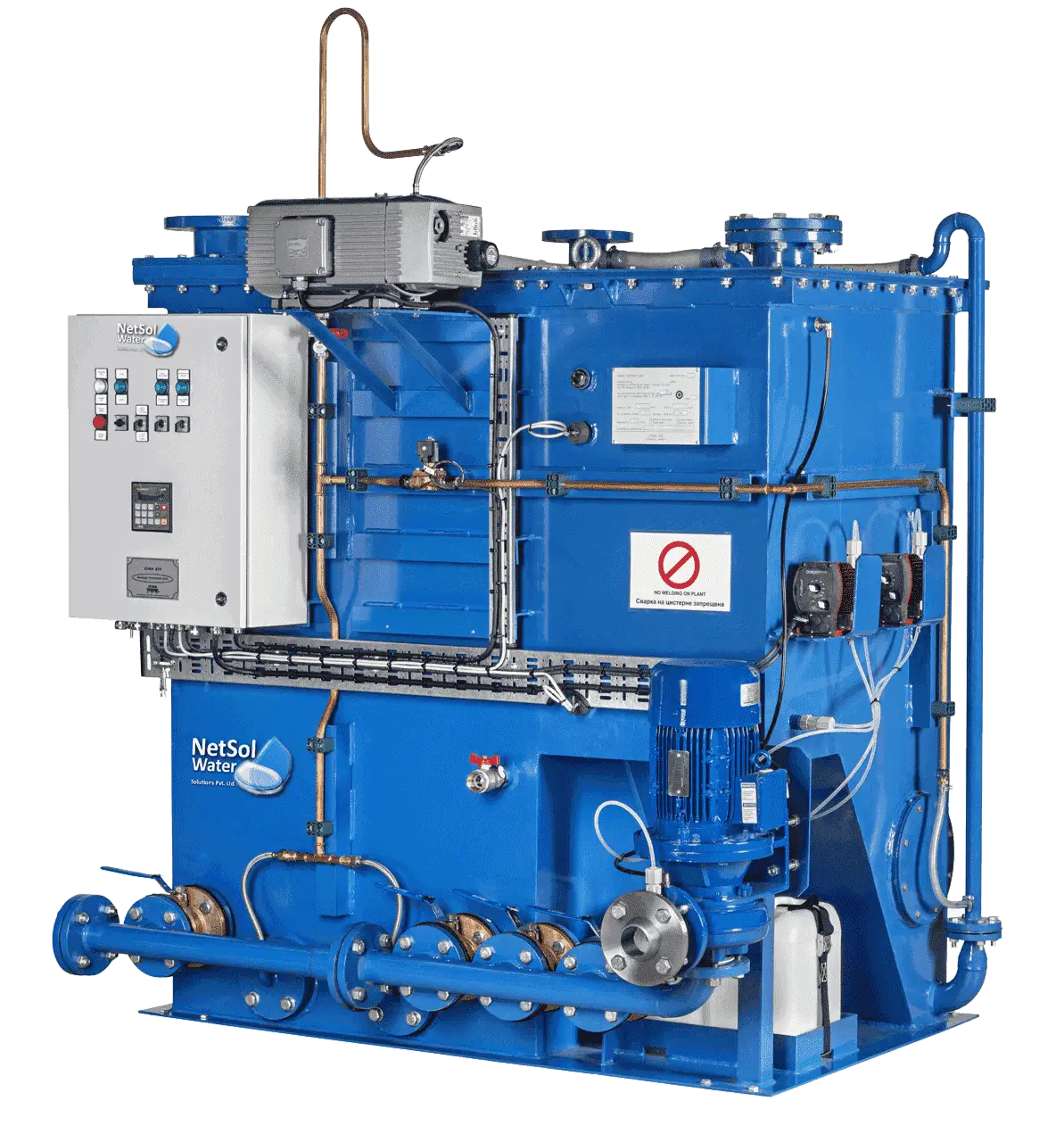
Finally let us take the example of waste management systems where Industry 4.0 can be witnessed through the automation of water treatment plants, sewage treatment plants, and effluent treatment plants. Industries need fewer workers to operate and monitor the waste management systems since they can be monitored from remote through advanced technologies. Automation also reduces the cost of operation and also increases the efficiency cum effectiveness of these waste management systems.

