How to remove Sulphates, Phosphates and Fluorides from wastewater?
Sulphate precipitation may be required before discharging into drains (affecting concrete), if the wastewater is to be reused (scaling), or even to meet particular discharge standards.
1: The most common technique, which includes high quantities of SO42-, is the cold precipitation of gypsum CaSO4, 2H2O by adding Ca2+ as lime (common in acidic water) or CaCl2 according to the following reaction:
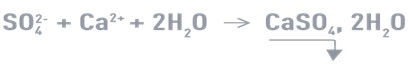
Precipitation occurs as heterogeneous crystals are extremely slow. This reaction must take place in the presence of a high concentration of seeds (> 20 g/l) to avoid supersaturation and harmful post precipitation.
The SO42– concentrations obtained will be affected by salinity, ionic activity of the medium, and excess Ca2-, for example, the residual values shown below can be obtained:
• 2 to 3 g/L SO42– in brackish water treatment applications where CaCl2 is used;
• 1.5 to 2.5 g/L SO42–when neutralizing acid water with lime but not CaCl2.
2: The precipitation of barium sulphate by adding BaCl2 is a second procedure. The obtained residual solubility’s are less than 20 mg/l, although the reagent is exceedingly costly and is rarely utilized.
In intermediate circumstances, permutation with a strong anionic resin SO42–/2Cl–can be considered at the expense of large Cl– and SO42– discharges.
Phosphate precipitation from wastewater
These salts can be found in a number of forms and concentration levels in wastewater:
-Phosphoric acid in phosphate fertilizer factory wastewater with HF and SiO2;
-Phosphates in domestic wastewater;
-Phosphates in boiler wastewater;
-In cooling circuits, polyphosphates and hexametaphosphates are used;
There are two possible modes of precipitation:
1: Acid effluents, through lime;
2: Non-acid water, through Al or Fe salts (formation of metal phosphates).
1: Precipitation using lime
There are two possible responses depending on the original acidity:
-Calcium dihydrogen-phosphate precipitation at an optimal pH of 6 to 7:

This chemical settles quickly but has a high residual solubility (130 to 300 mg/L as P2O5 depending on temperature);
-Tricalcium phosphate precipitation at an optimal pH of 9 to 12:
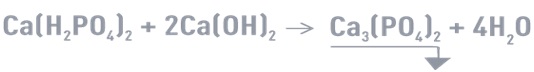
As a colloid, tricalcium phosphate has a residual solubility of a few mg/L. Even when a flocculent is introduced, it settles slowly.
2: Precipitation through Al3+ or Fe3+
Although AlPO4 and FePO4 are low-solubility salts, they will precipitate in colloidal form. The precipitate is removed by flocculating it over a metal hydroxide excess.
Fluoride precipitation from wastewater
Fluoride removal by precipitation involves acid effluents from incinerator gas scrubbing, aluminium (metallurgy), as well as the phosphoric acid, glass, and electronics sectors. In the final three situations, the presence of F– is invariably associated with a high quantity of silica, which changes precipitation circumstances. If we need to achieve low residual levels of F–, lime will always be employed as the neutralising agent, potentially enhanced by CaCl2:

These units have dimensions similar to those used for carbonate removal, although reaction durations will be longer.
What do we offer?
If you want to know more about the precipitation of sulphates, phosphates and chlorides from wastewater and how it can be handled,then you are at the right place!
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.



