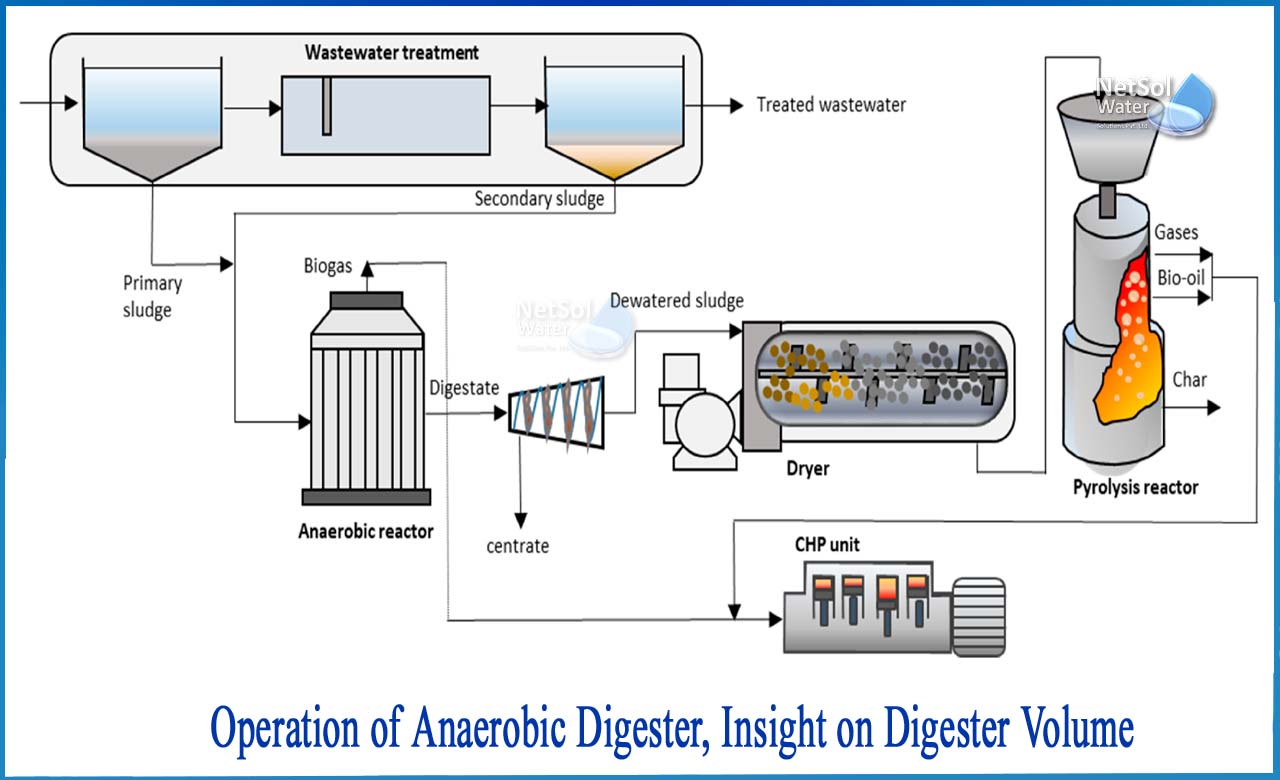
How does anaerobic digester work?
The organic material in a combination of primary settled sludge and biological sludge from the secondary clarifier is transformed to CH4 and CO2 under anaerobic conditions in the anaerobic digestion process. This is done in an oxygen-free environment in an airtight reactor.
Sludge is delivered constantly or intermittently into the reactor and held there for varied amounts of time. Liquefaction and gasification are two basic anaerobic digestion processes.The non-putrescible stabilized sludge that is removed constantly or intermittently from the process has a considerably decreased pathogen concentration. The biological oxidation of degradable organic sludge by microbes in anaerobic conditions is known as anaerobic digestion.
It happens when there is a lack of oxygen and organic matter serves as a source of food for microbes. The majority of the bacteria involved in this digestion are either obligatory anaerobes or facultative anaerobes. For the treatment of organic sludge, this method is used.
Operation related to Digesters
In general, digesters run at a temperature of 30 to 37 degrees Celsius and a pH of 7 to 7.2. The pH range for operations might be 6.7 to 7.4. To adjust the pH, lime can be applied.
Methanogenesis is inhibited and methane generation is reduced when the pH is reduced. The digester gas produced by the process can be utilized as a source of heat. Heavy metals can obstruct digestion, necessitating their removal at the source. Supernatant liquor has a BOD-5 concentration of around 2000 mg/L and SS concentration of 1000 mg/L, and it is recycled back into PST.
Acidification is usually avoided if the dry solids added or removed daily do not exceed 3 to 5% of the total dry solids in the digester.The amount of gas generated and the drop in VSS are used to determine the degree of digestion.
Digester volume
Total digester volume is determined by the amount of fresh sludge added daily, the volume of digested sludge produced daily and for the required digestion time, the volume of digested sludge storage, gas storage, and the volume of supernatant liquor.
In comparison to other types of storage, the volume of gas storage is quite modest.
The volume of leftover digesting sludge ‘Vs’, digestion time is a parabolic function if the supernatant liquid is eliminated as it is formed. The beginning volume minus 2/3 of the difference between the initial and final volume is the average volume of digested sludge.
Average volume of digested sludge:
Vavg=V1 -2/3 (V1-V2)
Where, V1 and V2 are the daily volumes of new sludge input and digested sludge generated (m3/day)
The release of water from the sludge solids and the breakdown and conversion of solids to biogas account for the majority of the sludge volume decrease during digestion.
As a result, the overall volume of sludge in digesters increases.
Vs-Vavg* td + V2 * ts
Where, Vs= Total Sludge volume, m3
V2= Volume of digested sludge, m3/d
Vavg= Avg. volume of digesting sludge
td= Time for required digestion, days
ts= Time provided for sludge storage, days
The bottom half of the digester is generally occupied by sludge, while the upper half is occupied by supernatant and biogas, resulting in
Vt = 2 V.
Where,Vt denotes the total digester volume in cubic meters, and m3 denotes the total digester volume in cubic meters.
Typical mean cell residence time and organic loading rates (kg VSS/m3.day) can also be used to build the digesters.
The mean cell residence time,
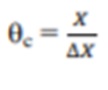
Where, X is the weight in kilogrammes of dry solids in the digester, and Y is the weight in kilogrammes of dry solids generated per day in the digested sludge, which is equal to the weight in kilogrammes of sludge discarded each day. Because there is no recycling, the SRT in the digester is equal to the HRT. There is a temperature-dependent minimum ‘c’ below which digestion will not proceed.
Suggested values of θc at different temperatures:
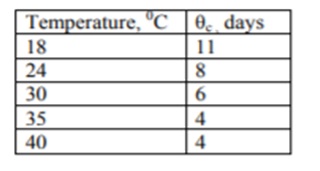
Because ‘c’ is a vital parameter, the actual value utilised in design is 2.5 times larger. As a result, the number of high-rate digesters is increasing.
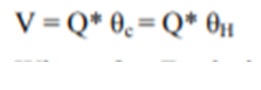

Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.