What are natural resources?
Natural resources are those that exist in the absence of human intervention. This encompasses the sources of valuable traits including economic and industrial utility, aesthetic value, scientific curiosity, and cultural worth. On Earth, it consists of sunshine, the atmosphere, water, land, all minerals, as well as all flora and animal life.
Natural resources as a part of natural heritage
Natural resources can be preserved as part of the natural heritage or in nature reserves. Biodiversity and geo-diversity are frequently found in the ecosystems of certain regions (such as the rainforest). Natural resources can be categorised in a variety of ways. Natural resources are materials and components (things that can be utilized) found in the environment. Natural resources are used to make every man-made product (at its fundamental level).
Occurrence of natural resources
A natural resource can exist as a separate entity, such as fresh water, air, or any living organism, such as a fish, or it can be transformed into an economically useful form that must be processed to obtain the resource, such as metal ores, rare-earth elements, petroleum, timber, and most forms of energy, by extractivist industries. Some resources are renewable, which implies they may be exploited at a specific pace and then restored by natural processes, however many extractive businesses rely largely on non-renewable resources that can only be taken once.
Distribution of natural resources
Natural-resource distributions can be at the heart of many economic and political disputes inside and between countries.This is especially true during times of increased scarcity and shortages (depletion and overconsumption of resources). Extraction of natural resources is also a major cause of human rights abuses and environmental degradation.
The Sustainable Development Goals and other international development agendas frequently focus on creating more sustainable resource extraction, with some scholars and researchers focusing on developing economic models, such as the circular economy, that rely less on resource extraction and more on reuse, recycling, and renewable resources that can be managed sustainably.
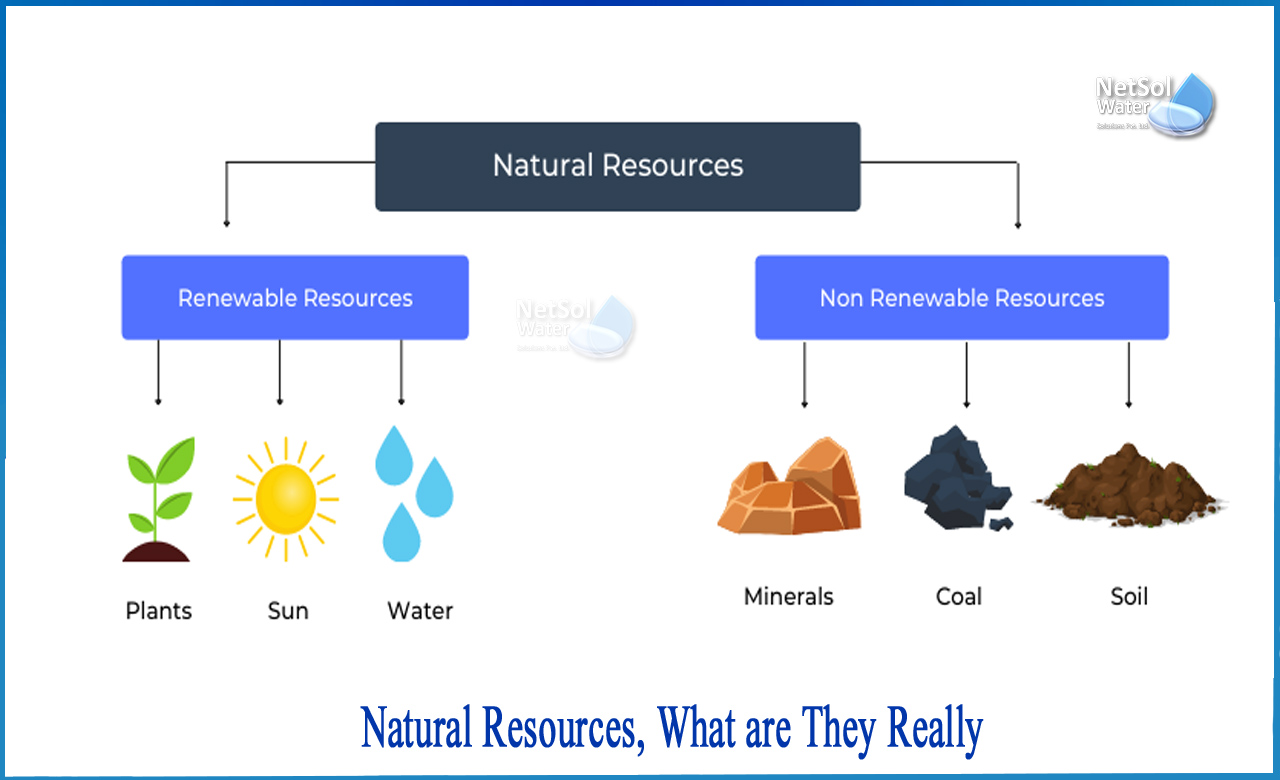
Natural resources are classified into two kinds based on their origin:
Biotic resources are derived from the biosphere (living and organic stuff), such as forests and animals, and the products derived from them.Because they are created from degraded biological matter, fossil fuels such as coal and petroleum are also included in this group.
Abiotic resources are those derived from non-living, non-organic substances. Land, fresh water, air, rare-earth elements, and heavy metals including ores such as gold, iron, copper, silver, and so on are examples of abiotic resources.
Depending on their state of development, natural resources can be referred in the following ways:
Potential resources are those that may be exploited in the future, such as petroleum in sedimentary rocks, which remains a potential resource until it is dug out and utilised.
Actual resources are those that have been surveyed, measured, and qualified and are now being utilized in development, such as wood processing, and are often dependent on technology.
Reserve resources – A portion of an existing resource that can be successfully developed in the future.
Stock resources – Those that have been surveyed but cannot be utilised owing to technological limitations.
Natural resources can be classified based on their pace of recovery as follows:
Renewable resources are those that can be renewed naturally. Some of these resources, such as sunshine, air, wind, and water, are always accessible and their amounts are unaffected by human usage. Although many renewable resources do not regenerate as quickly, they are vulnerable to depletion due to overuse. In terms of human usage, resources are considered as renewable if the pace of replenishment/recovery surpasses the rate of consumption. In comparison to non-renewable resources, they refill quickly.
Non-renewable resources – Non-renewable resources are either slow to develop or do not occur naturally in the environment. Minerals are the most prevalent type of resource in this category. From a human standpoint, resources are non-renewable when their rate of consumption exceeds their pace of replenishment/recovery; fossil fuels are an example of this because their rate of production is incredibly slow (possibly millions of years), making them non-renewable.
Conclusion
Some resources decrease spontaneously without human intervention, the most noteworthy of which are radioactive elements like uranium, which naturally decay into heavy metals. Metallic minerals, on the other hand, may be recycled and reused, but coal and petroleum cannot. It takes millions of years to refill them after they have been depleted.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.