WHAT IS HYDROPONICS?
Hydroponics is defined as the practice of growing plants using only water, nutrients, and a growing medium. The word hydroponics comes from the roots “hydro”, meaning water, and “ponos”, meaning labour. This method of growing plants doesn’t use soil. Instead of soil, hydroponic gardeners use different types of growing media, like coconut coir, vermiculite, perlite, and more. In a nutshell, the idea behind hydroponics is to remove as many barriers as possible between a plant’s roots and the water, oxygen, and nutrients it needs to grow (and thrive).This can be done in many different ways, which is why we’ll look at the different types of systems you can use to grow hydroponically — but first, let’s understand the benefits and downsides of growing without soil.
Types Of Hydroponic Systems
Six main types of hydroponic systems to choose from:
1- Wick Systems
2- Deep Water Culture (DWC)
3- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT).
4- Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain)
5- Aeroponics
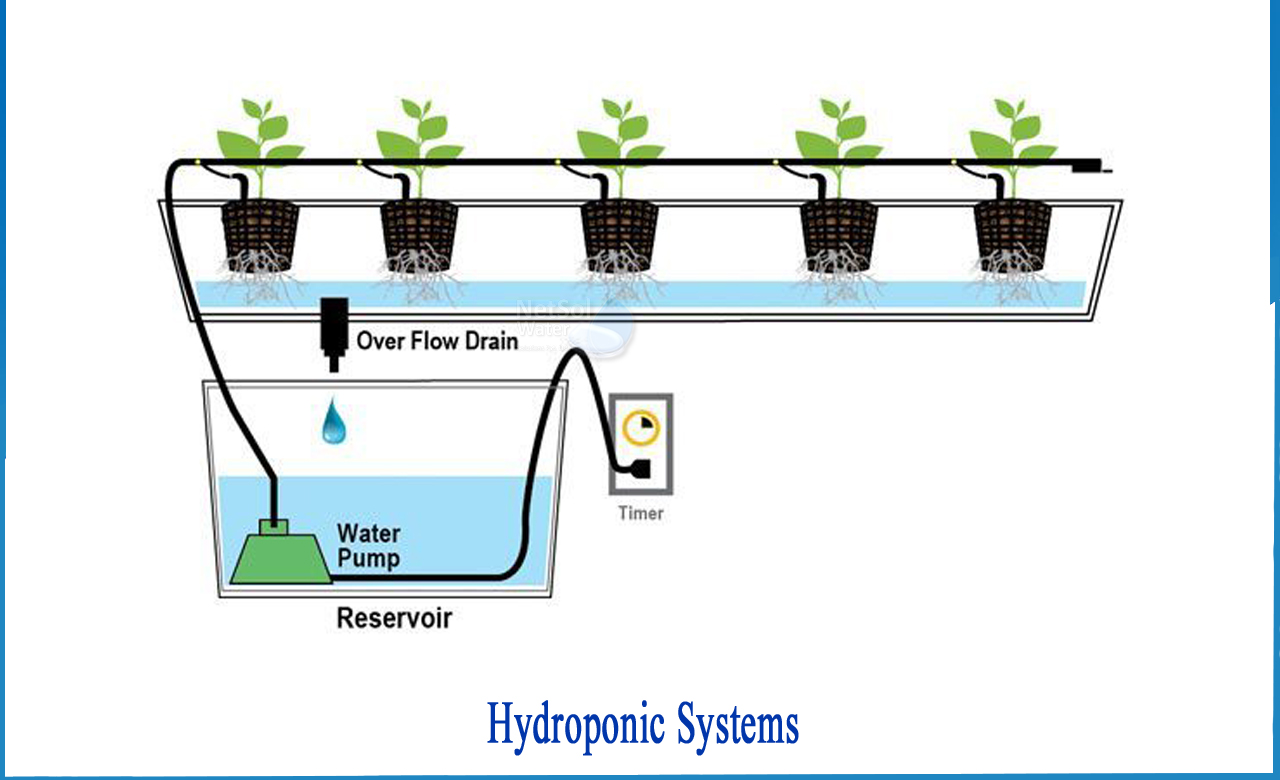
6- Drip Systems
WORKING
Hydroponic systems work by allowing minute control over environmental conditions like temperature and pH balance and maximized exposure to nutrients and water. Hydroponics operates under a very simple principle: provide plants exactly what they need when they need it. Hydroponics administers nutrient solutions tailored to the needs of the particular plant being grown. They allow you to control exactly how much light the plants receive and for how long. pH levels can be monitored and adjusted. In a highly customized and controlled environment, plant growth accelerates.
By controlling the environment of the plant, many risk factors are reduced. Plants grown in gardens and fields are introduced to a host of variables that negatively impact their health and growth. Fungus in the soil can spread diseases to plants. Wildlife like rabbits can plunder ripening vegetables from your garden. Pests like locusts can descend on crops and obliterate them in an afternoon. Hydroponic systems end the unpredictability of growing plants outdoors and in the earth. Without the mechanical resistance of the soil, seedlings can mature much faster. By eliminating pesticides, hydroponics produce much healthier and high-quality fruits and vegetables. Without obstacles, plants are free to grow vigorously and rapidly.
COMPONENTS OF A HYDROPONIC SYSTEM
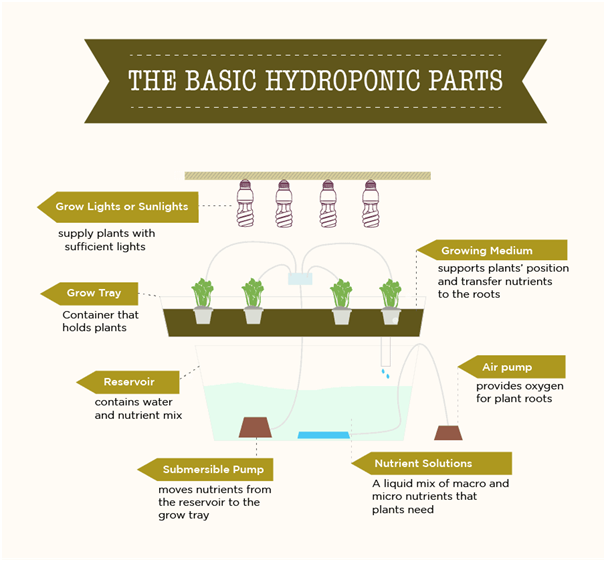
To maintain a flourishing hydroponic system, you will need to become acquainted with a few components that make hydroponics run efficiently.
GROWING MEDIA
Hydroponic plants are often grown in inert media that support the plant’s weight and anchor its root structure. Growing media is the substitute for soil, however, it does not provide any independent nutrition to the plant. Instead, this porous media retains moisture and nutrients from the nutrient solution which it then delivers to the plant.
AIR STONES AND AIR PUMPS
Plants that are submerged in water can quickly drown if the water is not sufficiently aerated. Air stones disperse tiny bubbles of dissolved oxygen throughout your nutrient solution reservoir. These bubbles also help evenly distribute the dissolved nutrients in the solution.
NET POTS
Net pots are mesh planters that hold hydroponic plants. The latticed material allows roots to grow out of the sides and bottom of the pot, giving greater exposure to oxygen and nutrients. Net pots also provide superior drainage compared to traditional clay or plastic pots.