What is grey water?
Greywater or sullage is domestic wastewater generated in households or office buildings from streams free of faeces, i.e., all streams except toilet wastewater. Sinks, showers, baths, washing machines, and dishwashers are all sources of greywater. Greywater is usually safer to handle and easier to treat and reuse onsite for toilet flushing, landscape or crop irrigation, and other non-potable uses because it contains fewer pathogens than domestic wastewater. Greywater may still contain pathogens from soiled clothing or cleaning the anal area in the shower or bath.
Can grey water be reused?
Global water resource availability is deteriorating. According to one report, water scarcity will affect 2.7 billion people by 2025, affecting one out of every three people on the planet. Reusing greywater has proven to be an effective solution to this problem, and wastewater reuse is also known as recycled or reclaimed water.
Is using grey water legal?
Reusing greywater is legal in many states that are prone to drought. There is a risk associated with greywater, and it is much easier [for regulators] to say no than it is to say yes to something they are unfamiliar with. It's a mental shift and a shift in how we've viewed water for a long time.
When you live in a state where there is a scarcity of water or a drought, it is easier to persuade people to try something new. In states where grey water usage is legal, one must strictly adhere to the guidelines.
There are restrictions on the number of organisms that can be present in the water as part of its irrigation water quality requirements, so disinfection, as well as a permit, are usually required to use greywater for irrigation.
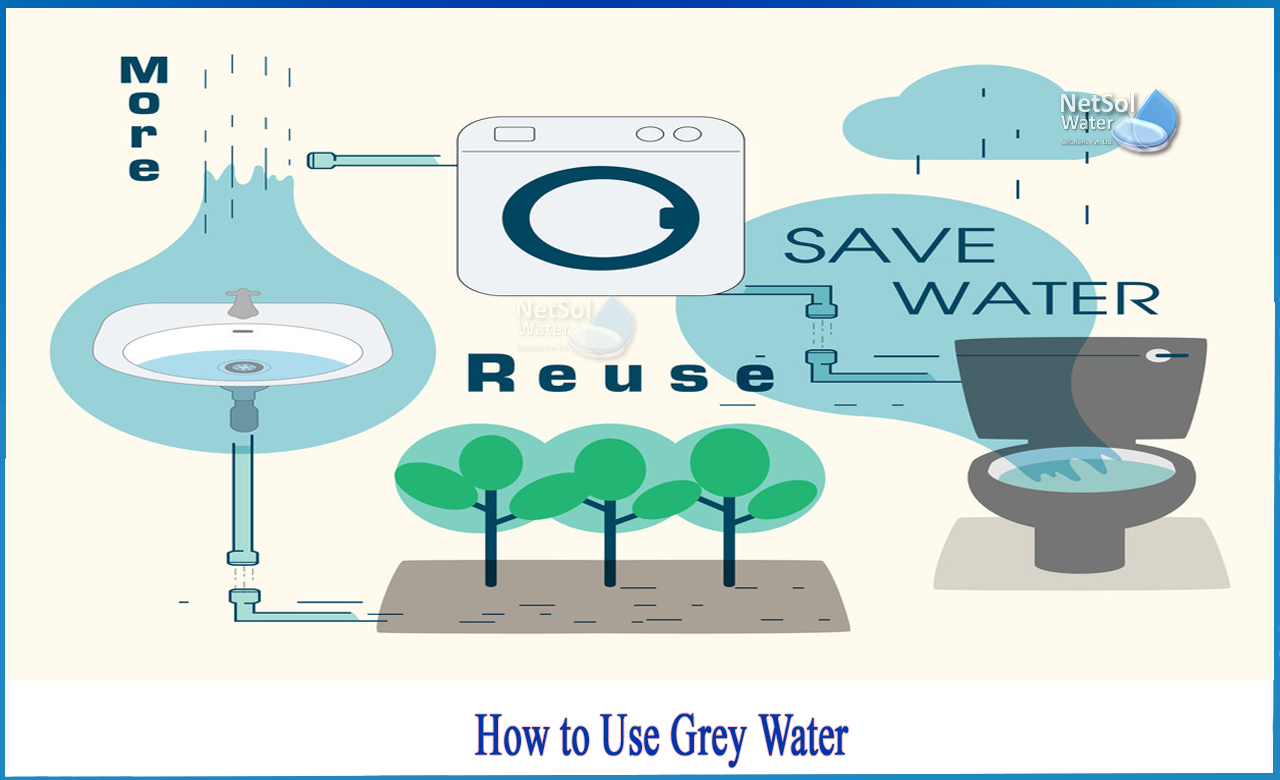
How to reuse grey water?
If you want to reuse greywater for irrigation, you must use plant-friendly products, or those that don't contain a lot of salt, boron, or chlorine bleach, which can harm plants. Greywater reuse in urban water systems has significant benefits for both the water supply subsystem, which reduces the demand for fresh clean water, and the wastewater subsystem, which reduces the amount of wastewater that must be conveyed and treated. Greywater can be used for a variety of purposes, including toilet flushing and irrigation.
1-Irrigation
Greywater should be applied below the surface whenever possible (e.g., via drip line on top of the soil, under mulch, or in mulch-filled trenches) rather than sprayed, as inhaling the water as an aerosol poses a risk. To reduce pH, soils watered by greywater systems can be amended with gypsum (calcium sulphate). Ammonia-containing cleaning products are safe to use because plants can use it to obtain nitrogen. Some greywater may be applied directly from the sink to the garden or container field, where it will be treated further by soil life and plant roots. To protect vegetation when reusing greywater for irrigation, use non-toxic and low-sodium soap and personal care products.
2-Indoor
For the average household, a greywater system could save up to 30% on water consumption.
Using:
· Eliminates the risk of biological contamination.
· A cleaning tank is used to remove floating and sinking items.
In certain dwellings, greywater recycling without treatment is used for applications where potable water is not required (e.g., garden and land irrigation, toilet flushing). It may also be used in dwellings when the greywater (for example, from rainwater) is already relatively clean and/or has not been polluted with non-biodegradable chemicals such as non-natural soaps (thus using natural cleaning products instead).
It is not recommended to use water that has been in the greywater filtration system for more than 24 hours because bacteria can grow and affect the water.
For more details, contact us at Netsol Water.