How does electrocoagulation prove an effective method for WWT?
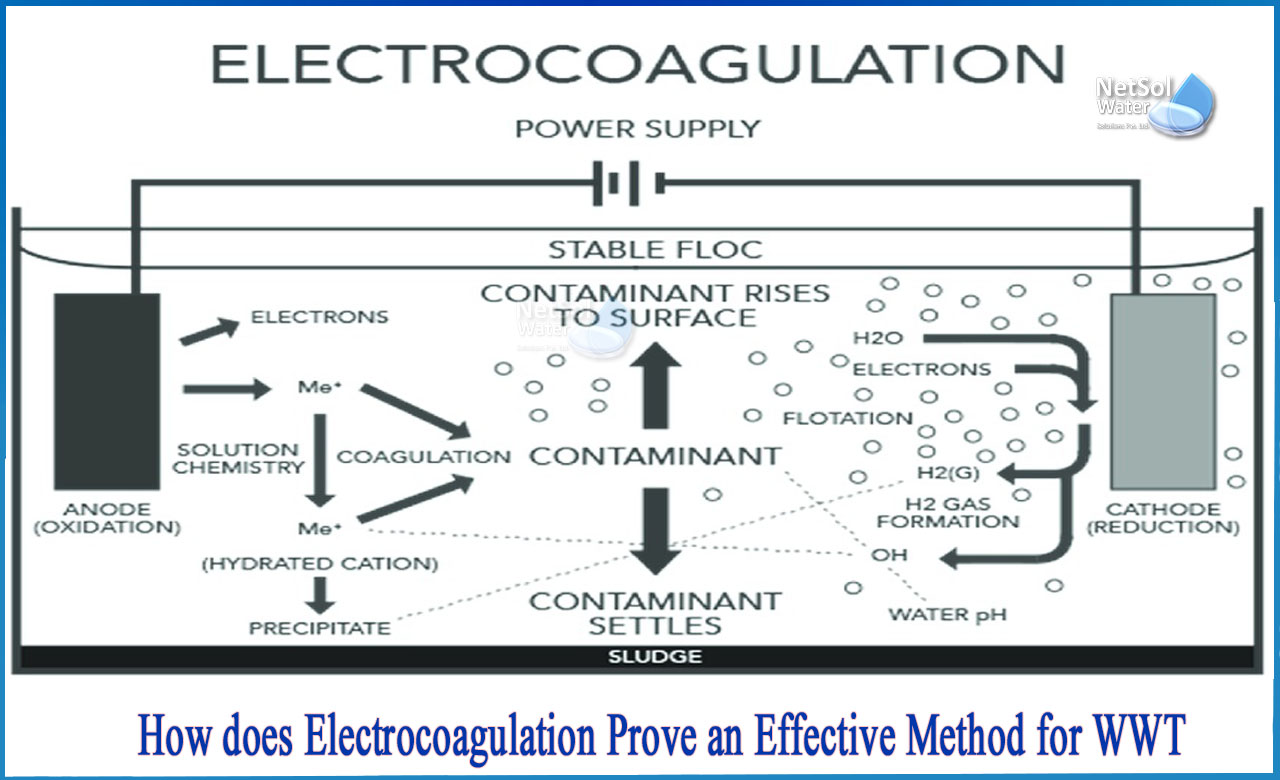
Electrocoagulation is an alternative wastewater treatment method. It entails the destabilization of water contaminants that are already suspended, emulsified, or dissolved by the action of a low voltage, direct electric current and sacrificial metallic electrodes, typically aluminum or iron.
How is this process useful?
A small device produces electrocoagulation by using a specially designed reactor in which metal plates or metallic electrodes are placed. This process produces a high concentration of cations, which destabilize residual pollutants in water, forming complex hydroxides capable of adsorption and producing aggregates (flocs) with contaminants. On the other hand, gas forms, causing turbulence and pushing floc to the surface.
What are the various advantages?
Another fantastic advantage of the electrocoagulation process is chemical oxidation, which oxidizes metals and non-toxic pollutants while also significantly reducing COD/BOD.
Following the electrocoagulation process, waste is obtained in an aqueous form composed of chemical species of iron bound to arsenic. This waste must be treated using conventional techniques to separate as much water as possible while producing an easy-to-manage byproduct in the smallest possible volume.
Electrocoagulation is a straightforward procedure that necessitates the use of basic equipment. Because electro coagulated flocs contain less surface water, these are acid-resistant, and more stable, they can be separated more easily by filtration. Furthermore, it is a low-cost technology that requires little investment and upkeep.Aside from being a wastewater treatment technique, electrocoagulation has also become a very interesting process to use prior to reverse osmosis because it facilitates the process of desalination of the water to be treated.
Electro coagulation (EC) is a one-of-a-kind method for water and wastewater treatment that is based on the electrochemical dissolution of sacrificial metal electrodes into soluble or insoluble species, which improves coagulation, precipitation, or adsorption of colloidal contaminants.
The coagulating ions are generated continuously in an electro coagulation process, which consists of three steps:
· Electrolytic oxidation of the sacrificial anode results in the formation of a coagulant
· Pollutant destabilization, particulate suspension, and emulsion breaking
· Destabilized phases aggregate to form flocs.
The following summarizes the destabilization mechanisms of contaminants, particulate suspension, and emulsion breaking:
1. The ions produced by the oxidation of the sacrificial anode cause diffuse double layer compression around the charged species.
2. Neutralization of ionic group charge in wastewater by counter ions formed by electrochemical dissolution of the sacrificial electrode. These counterions reduce the electrostatic interaction.
3. Increased particle repulsion to the point where Van der Waals attraction predominates, causing coagulation in the solution. As a result of the process, there is no net charge.
4. The formation of floc as a result of coagulation results in the formation of a blanket of sludge that entraps and bridges colloidal particles that remain in the solution. The hydroxides, oxyhydroxides, and solid oxides provide active surfaces for polluting species adsorption.
Treatment Parameters in the Electrocoagulation (EC) Process
There are numerous treatment parameters to consider. The following are the effects of electro coagulation on the efficiency of removing contaminants from water or wastewater:
1. The electrodes can be made of iron, aluminum, or an inert material. The chemistries and applications of iron and aluminum ions and hydroxides differ.
2. The solution's pH affects the dissolution of aluminum electrodes, the potential of colloidal particles, and the speciation of metal hydroxides in the solution.
3. The number of electrochemical reactions occurring on the electrode surface is proportional to the current density.
4. Treatment time is proportional to the amount of coagulants formed in the electrocoagulation system as well as other reactions occurring in the system.
5. Temperature influences floc formation, solution conductivity, and reaction rates. Depending on the pollutant, rising temperatures can have a positive or negative impact on removal efficiency.
6. Electrode potential determines which reactions taking place on the electrode surface.
7. Pollutant concentration influences removal efficiency because coagulation does not follow zero-order reaction kinetics but rather pseudo second or first-order kinetics.
8. Inter-electrode distance may have an effect on treatment efficiency and electricity consumption.
Metals, suspended particles, clay minerals, organic matter, and oil and greases can be effectively removed from a variety of industrial effluents using electro coagulation.
For more information on waste water related products, contact Netsol Water.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.