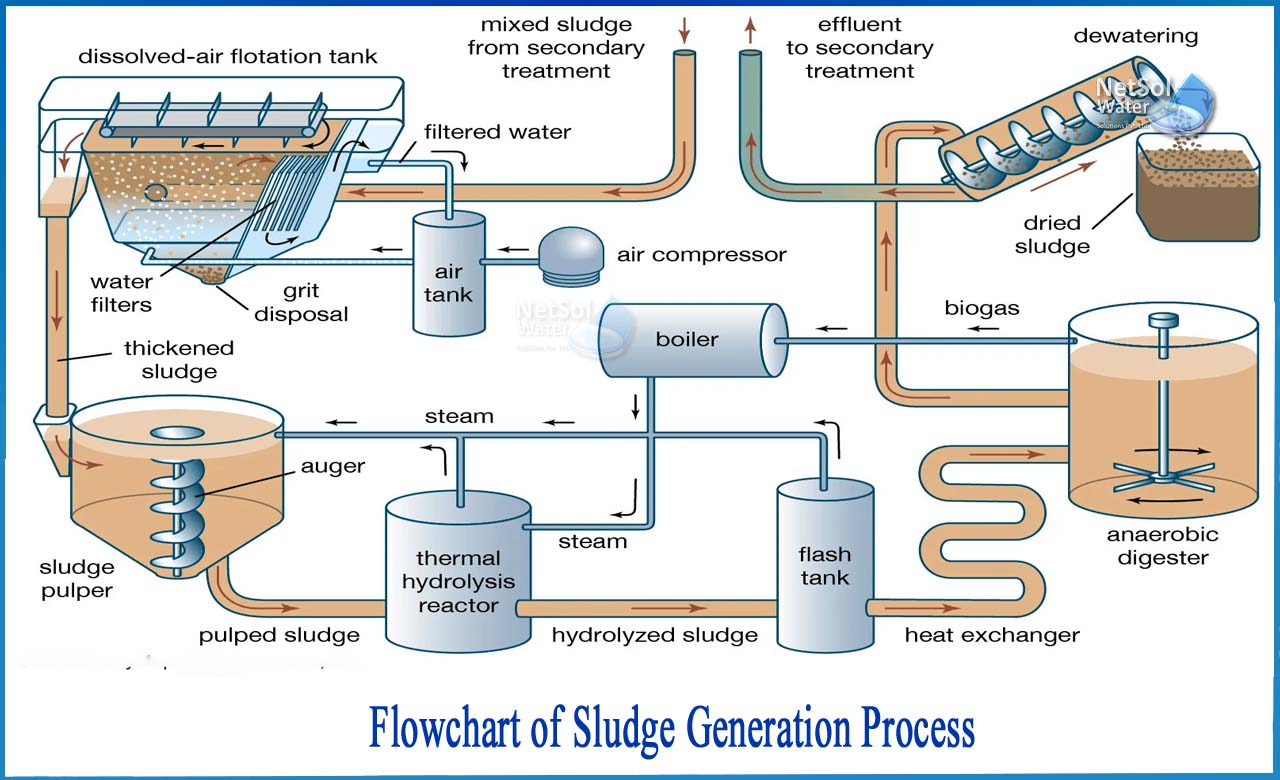
What is Sludge Generation process?
Sewage sludge treatment describes the process for treating and disposing of sewage sludge generated during wastewater treatment. Sludge treatment focuses on reducing the weight and quantity of sludge, reducing transportation and disposal costs, and reducing the potential health risks of disposal options. Moisture removal is the primary means of reducing weight and volume, but pathogen destruction is often achieved by thermophilic digestion, composting, or heating during incineration.
The choice of sludge treatment method depends on the amount of sludge generated and the treatment cost required for the available disposal options. Air drying and composting may be attractive to rural communities, but limited land availability favours urban anaerobic digestion and mechanical dehydration. Economics ofa large scale energy are in metropolitan areas which may facilitate recovery alternatives.
What is sludge composed of?
Sludge is mainly composed of water, and a certain amount of solid matter, which is removed from the waste liquid.
P?rimary sludge contains perceptible solids that are removed during the primary treatment in the primary purification equipment.
Secondary sludge is sludge deposited in post-treatment bioreactors or secondary purification equipment used in inorganic oxidant processes.
In an intensive wastewater treatment process, the capacity of the liquid line's tank is not sufficient to store sludge, so the resulting sludge must be continuously removed from the liquid line. This is done to keep the processing process compact and balanced (sludge generation is similar to sludge removal). Sludge removed from the liquid line is sent to the sludge processing line.
Steps of Sludge generation
1. Preliminary treatment and primary treatment
In this process the primary class of sludge is generated called primary sludge. This sludge consists of grits and solid particles.
2. Secondary treatment and sludge
This sludge is generated by the secondary treatment of the waste and sewage and contains organic matter. This sludge is digested using aerobic, anaerobic and facultativebacteria.
This sludge is most important sludge type as it is produced from biological treatment and its correct disposal is necessary. This sludge contains activated biomass and negative effects are generated if processes are not followed correctly or if there is any change in the waste characteristics.
This sludge is of three types: Generated by aerobic bacteria, generated by anaerobic bacteria and the ones developed by facultative bacteria. Also, there is a concept of return sludge, which is returned to the treatment unit as a seed for secondary treatment of next batch of waste.
3. Tertiary sludge
This sludge is generated by the tertiary treatment of waste. This sludge can be disposed of without much further sludge treatment.
Difference between primary, secondary and tertiary sludge
Biological wastewater treatment produces different sorts of sludge within the individual process steps. Raw sludge is untreated non-stabilized sludge, which can be taken from wastewater treatment plants. It tends to acidify digestion and produces odour.
What are the different types of sludge?
1: Primary sludge
Primary sludge is produced through the mechanical or primary wastewater treatment process. It occurs after pre-treatmentand is composed of undissolved wastewater impurities. The sludge that builds up on the bottom of the primary purifier is also called primary sludge. The composition of this mud depends on the characteristics of the catchment area. Primary sludge is high in organic matter such as faeces, vegetables, fruits, fibre and paper. Viscosity is a viscous liquid with a water content of 93% to 97%. Primary sludge is a result of the confinement of suspended solids and organics in the primary treatment process through gravitational sedimentation, commonly by a primary clarifier.
2: Secondary sludge
The secondary treatment process uses microorganisms to consume the organic matter in the wastewater.
a): Activated Sludge
The removal of dissolved organic matter and nutrients from the wastewater takes place in the biological treatment step. Organic matter removal is achieved by different types of bacteria and microorganisms, which require oxygen to live, grow and multiply in order to consume the organic matter. The effluent sludge from this process is called activated sludge. The activated sludge exists normally as flakes, which besides living and dead biomass contains adsorbed, stored, as well as organic and mineral parts. The sedimentation behaviour of the activated sludge flakes is important for the function of the biological treatment. The flakes must be simply removable, so that the biomass can be separated from the cleaned wastewater without problems and a required volume of activated sludge can be pumped back into the aerated part.
b): Return activated sludge
The activated sludge flows from the biological aeration basin into the final clarifier. The activated sludge flakes settle down to the bottom of the treatment unit and can be separated from the cleaned wastewater. The main part of the separated sludge, which is returned back to the aeration basin, is called return activated sludge. Excess secondary sludge is sent for further treatment and disposal.
To reach a constant sludge age, the unused biomass has to be removed from the biological or secondary treatment system as excess sludge which is disposed off. Excess sludge contains metabolically non-hydrolysable particulate matter and biomass.
c):Digestive Sludge
Anaerobic digestion produces digestive sludge. The colour is black and it smells earthy. The organic solid content of anaerobic sludge is 45-60%, depending on the degree of stabilization.
3:Tertiary sludge
Tertiary sludge results from further wastewater treatment steps by adding flocculants.
Conclusion
There are three basic biological treatment methods: the trickling filter, the activated sludge process, and the oxidation pond.
Primary sludge is generated from chemical coagulation and precipitation, sedimentation, and other primary processes, whereas secondary sludge is the activated waste biomass resulting from biological treatments.
How can Netsol Water ]help?
Netsol is India’s leading water and wastewater treatment solution company which covers all the needs of any water treatment scheme on all levels. We have the expertise to provide wastewater solutions at domestic, industrial and municipal level.
Netsol Water is Greater Noida-based leading water & wastewater treatment plant manufacturer. We are industry's most demanding company based on client review and work quality. We are known as best commercial RO plant manufacturers, industrial RO plant manufacturer, sewage treatment plant manufacturer, Water Softener Plant Manufacturers and effluent treatment plant manufacturers. Apart from this 24x7 customer support is our USP. Call on +91-9650608473, or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com for any support, inquiry or product-purchase related query.