Effluent Treatment Plant for Chocolate manufacturing unit
The wastewater in the chocolate manufacture industry can be characterized as non-toxic as it contains no hazardous ingredients, but if it contains a substantial amount of total solids (TS), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD). In various stages, including harvesting, cleaning, fermenting, drying, roasting, grinding, pressing, pulverizing, and blending, the production of chocolate uses industry water. So industrial wastewater treatment must be a sustainable procedure.
In this blog, we will discuss in detail the working function of ETP for Chocolate manufacturing unit.
Working function of ETP for Chocolate manufacturing unit:
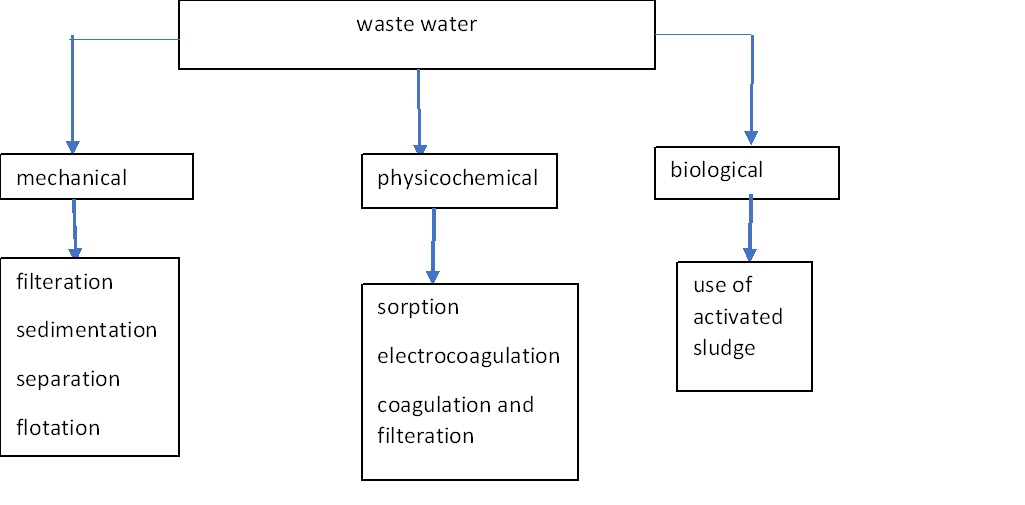
Mechanical treatment:
Mechanical wastewater treatment, commonly referred to as the first stage of purification, aims to remove bigger floating and dragging substances, granular particles larger than 0.1 mm in diameter, and suspensions, oily substances, and fatty acids that fall easily. This is accomplished using grates and screens, which collect and separate solid waste from the bulk wastewater. At this stage, filtration, drainage, sedimentation, and flotation are all completed.
Physicochemical treatment:
1. Sorption
There are two separate phenomena that make up sorption. The first is adsorption, which is the process by which molecules adhere to the surface of a solid or liquid. The creation of any continuous phase as a result of the sorption of one material by another is known as absorption, which is the second process. Because they are straightforward and don't need a high operating temperature, adsorption-based technologies are thought to be among the most competitive.
2. Coagulation and flocculation
These methods are mostly used in wastewater treatment to get rid of organic contaminants and suspended pollutants. The coagulant employed determines how well a procedure works. The most popular materials are active silica, aluminium, and iron salts.
3. Electrocoagulation
The electrochemical method of electrocoagulation (EC) for treating wastewater is gaining popularity. Iron or aluminium anodes that have been electrolytically dissolved are typically employed in the EC, which is a straightforward and effective process. The coagulating agent is created in situ by electro-oxidation of a sacrificial anode, therefore no additional chemical coagulants or flocculants are required.
4. Ozonation
Utilized in wastewater treatment, ozone is a strong oxidant that is readily soluble in water. Water that has been diluted well before ozonation works best. This method can only be used in wastewater with a high concentration of organic components as a preliminary stage in the full treatment technology.
Biological methods:
1. The application of activated sludge
Although the costs of acquisition and operation are occasionally prohibitive for industrial applications, activated sludge treatment under aerobic conditions is one of the most often used procedures. Physical and metabolic processes are present in the biological system known as activated sludge. On the surface of flocks, physical processes based on the adsorption of organic molecules cause them to fragment into smaller pieces. They undergo another metamorphosis after being taken up by microbial cells.
2. Treatment in an anaerobic environment
The anaerobic treatment converts organic waste in sewage into biogas by a microbial process, such as methane fermentation. (methane and CO2). Both flocculent and granular bacteria are present in anaerobic sludge and contribute to the process.
Numerous wastewater treatment processes employ anaerobic technologies. Various wastes, including biosolids, can be treated via anaerobic digestion.
Process flow diagram of ETP for Chocolate manufacturing unit
Do you need an advice or assistance on selecting the best water and waste water treatment unit? We have solutions for all your problems!
Let us now your problem, our experts will make sure that it goes away.
For an assistance or related query,
Call on +91-965-060-8473
Or write us at enquiry@netsolwater.com



