Difference between Distillation vs Filtration
Filtration and distillation have nothing in common except that they are both separation techniques. Briefly both processes can be defined as:
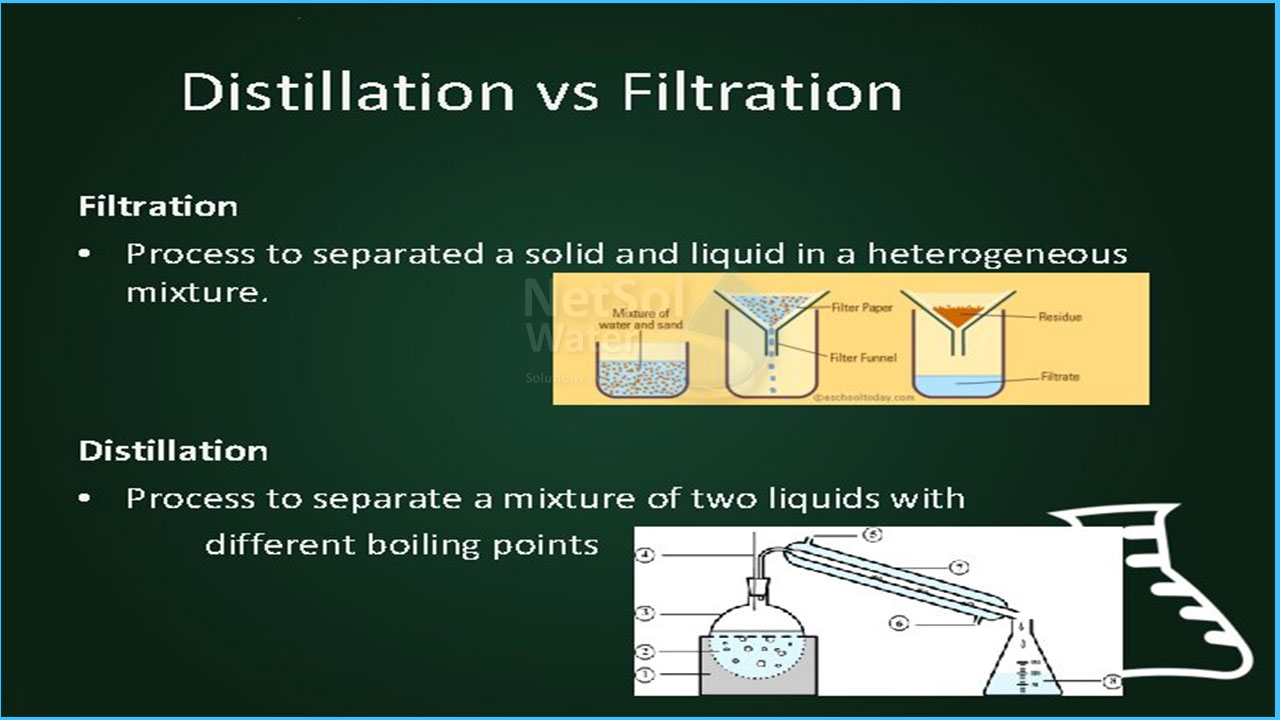
Filtration is a physical process in which a liquid containing suspended solid particles is passed through a fine screen to separate the solid from the liquid and Distillation is a method of separating liquids by converting the mixture's physical state from liquid to gas.
The real life applications of both the processes will clearly state the difference between filtration and distillation, which goes like this
1-Distillation
The more volatile component of the mixture—that is, the one that can be vaporised more easily—is separated from the less volatile component during distillation. In the above depiction of separating water from salt, the water is clearly the more volatile component: its boiling point is much, much lower than that of salt, and the heat necessary to vaporise the salt is so large that the water would have been vaporised long before the salt was impacted. After the volatile component has been vaporised or converted to distillate, it goes through condensation, which is the cooling of a gas to become a liquid, followed by the collection of the liquid or condensate. Heat is the agent of separation in all of these stages of distillation. This is especially significant in the fractional distillation process.
If distillation can separate water from salt, it can presumably also separate water from microorganisms and other pollutants via a more sophisticated rectification process. One of the most common uses of the distillation process is the purchase of distilled water for drinking and other reasons.
The production of ethyl alcohol is another well-known use of this method, made famous (or possibly notorious) by stories of bootleggers making homemade whiskey in the woods from "stills" or distilleries. To separate the hydrocarbons benzene and toluene, as well as acetone from acetic acid, distillation is used. Distillation separates the lighter protium isotope, or ordinary hydrogen, from the heavier deuterium in nuclear power plants that require large amounts of the hydrogen isotope deuterium. The petroleum sector, on the other hand, makes extensive use of distillation.
2-Filtration
A suspension (solid particles floating in a liquid) is permitted to flow through filter paper suspended in a glass funnel in the simplest kind of filtration. The solid particles are trapped by the filter paper, which allows a clear solution (the filtrate) to flow through the funnel and into a receiving container. Filtration has one of two purposes: to catch solid material suspended in fluid or to clear the fluid in which the solid is suspended.
Gravitational filtration is commonly used for water purification. Water is usually let to run down through a thick layer of granular material like sand, gravel, or charcoal to eliminate pollutants. A typical equipment, the vacuum cleaner, uses gas filtration to push a stream of dust-filled air through a filtering bag inside the machine. This is the same idea that is used in air filters as well as air conditioning and heating systems. Gas filtration is used in a variety of sectors to cleanse items released into the atmosphere as well as the air in the workplace.