Design an Effluent Treatment Plant for Rice Mill
An Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) is a crucial component in the treatment and disposal of industrial wastewater. In this blog, we will design an ETP for a rice mill, including a process flow diagram and a detailed explanation of its working function.
Process Flow Diagram
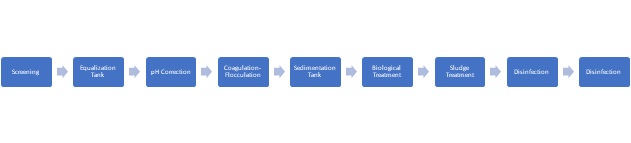
The process flow diagram for the ETP of a rice mill is as follows:
- Screening: The first step in the treatment process is the removal of large solids such as stones, sticks, and other debris from the wastewater stream. This is done using a bar screen or a grit chamber.
- Equalization Tank: The wastewater is then collected in an equalization tank, where it is mixed and homogenized. This helps in maintaining a consistent flow rate and pH level of the wastewater.
- pH Correction: The pH level of the wastewater is then adjusted using chemicals such as lime or sulfuric acid. This helps in the removal of dissolved solids and heavy metals from the wastewater.
- Coagulation-Flocculation: In this step, chemicals such as alum or ferric chloride are added to the wastewater to form a gelatinous mass called floc. The floc particles attract and trap the suspended solids, and the floc settles to the bottom of the tank.
- Sedimentation Tank: The settled floc is then removed from the wastewater stream using a sedimentation tank. The clarified water is then discharged to the next stage of treatment.
- Biological Treatment: In the biological treatment stage, the wastewater is treated using microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi. The microorganisms consume and break down the organic matter present in the wastewater, producing carbon dioxide and water as byproducts.
- Sludge Treatment: The excess sludge generated during the treatment process is then removed and sent to a sludge treatment system. The sludge is either disposed of or used as a fertilizer in agriculture.
- Disinfection: The final stage in the treatment process is disinfection, where the treated wastewater is disinfected using chemicals such as chlorine or ozone. This helps in the removal of any remaining pathogens and bacteria in the wastewater.
Working Function
The ETP for a rice mill functions by treating the wastewater generated during the rice milling process. The wastewater contains a high concentration of suspended solids, organic matter, and heavy metals, which need to be removed before the wastewater can be safely discharged into the environment.
The wastewater is first screened to remove large solids and then collected in an equalization tank, where it is mixed and homogenized. The pH level of the wastewater is then adjusted using chemicals, and coagulants are added to the wastewater to form floc particles.
The floc particles are then settled in a sedimentation tank, and the clarified water is then discharged to the next stage of treatment. The wastewater is then treated using microorganisms in the biological treatment stage, and the excess sludge is removed and treated separately.
Finally, the treated wastewater is disinfected using chemicals, and the clean water is discharged into the environment. The ETP for a rice mill is designed to ensure that the wastewater generated during the rice milling process is treated and discharged safely into the environment, without causing any harm to the environment or the public health.
Conclusion
The design of an Effluent Treatment Plant for a rice mill involves several stages of treatment, including screening, equalization, pH correction, coagulation-flocculation, sedimentation, biological treatment, sludge treatment, and disinfection. The process flow diagram and working function of the ETP for a rice mill are crucial in ensuring that the wastewater generated during the rice milling process is treated and discharged safely into the environment, without causing any harm to the environment or public health.
For any other support, inquiries, or product purchases, call on +91-9650608473 or email at enquiry@netsolwater.com



