Design an ETP for Gold or Diamond manufacturing industry
The manufacturing of gold and diamond products involves various complex processes that generate significant amounts of wastewater. The wastewater generated in this industry contains a range of impurities, including heavy metals, organic matter, and chemicals, which can be harmful to the environment if discharged untreated. It is therefore necessary to design an effluent treatment plant to remove these impurities before discharging the treated water into the receiving water body.
The design of an effluent treatment plant for the gold and diamond manufacturing industry requires a comprehensive understanding of the wastewater characteristics, the regulatory requirements, and the treatment technologies available.
This blog will provide a detailed design basis process flow diagram and working functions for such a plant, outlining the primary treatment, chemical treatment, sedimentation, filtration, reverse osmosis, and disinfection processes involved.
Basis process flow diagram:
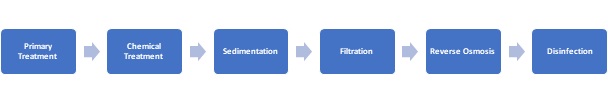
1- Primary Treatment: The first stage of the effluent treatment plant is primary treatment. The wastewater is screened to remove any large solids and then passed through a grit chamber to remove sand and other heavy particles. After that, the wastewater is sent to an equalization tank, which helps to balance the flow rate and load of the wastewater.
2- Chemical Treatment: The wastewater is then treated with chemicals to remove any heavy metals and other impurities. Coagulants are added to the wastewater to destabilize the particles, and flocculants are added to form larger flocs that can be easily removed by sedimentation or filtration. The chemical treatment process also helps to remove any organic matter and suspended solids from the wastewater.
3- Sedimentation: The wastewater is then transferred to a sedimentation tank, where the flocs settle to the bottom of the tank, and the clarified water is removed from the top. The sedimentation process removes any remaining suspended solids and organic matter.
4- Filtration: The wastewater is then passed through various filters, such as activated carbon filters, to remove any remaining impurities, including chemicals, heavy metals, and organic matter.
5- Reverse Osmosis: The wastewater is then treated with reverse osmosis to remove dissolved impurities, such as salts and minerals, from the wastewater. In this process, the wastewater is passed through a semi-permeable membrane, which removes the impurities and produces clean water.
6- Disinfection: The final stage of the effluent treatment plant is disinfection. The treated wastewater is disinfected using ultraviolet (UV) or chlorine to kill any remaining pathogens and bacteria. The treated water is then stored in an effluent storage tank before being discharged into the receiving water body.
Conclusion:
The design of an effluent treatment plant for the gold and diamond manufacturing industry requires careful consideration of the specific wastewater characteristics and the discharge limits set by the regulatory bodies. The process flow diagram and working functions provided in this blog provide a comprehensive overview of the design of such a plant.
It is important to note that the design of an effluent treatment plant may vary depending on the specific requirements of the industry and the regulations in the area. Therefore, it is essential to consult with a qualified professional and obtain the necessary permits before designing and constructing an effluent treatment plant.
You may reach us by phone at +91-9650608473 or by email at enquiry@netsolwater.com if you have any questions about our products, services, or support.



