What is sludge?
Sludge is a semi-solid slurry created by a variety of industrial processes, including water treatment, wastewater treatment, on-site sanitation systems, and so on. Sludge is made up of semi-solids like faeces that settle during wastewater treatment.
Removal of sludge
Scrapers are used to remove the sludge, which is then transferred to a tank where anaerobic bacteria degrade it to make biogas. This biogas is used as a low-cost source of energy for heating, cooking, and other purposes. It is also employed in the generation of energy.
Because it contains nutrient-rich organic elements, dried sludge is used as manure instead of taking up space in a landfill or other disposal site to restore and sustain productive soils and stimulate plant growth.
Handling of sludge
During the purification of surface water for potable supplies, a large amount of sludge is produced in water treatment plants. Municipalities, plant operators, and environmentalists must all pay close attention to the handling and disposal of sludge. It is critical to quantify the sludge produced at treatment plants in order to create appropriate management strategies for its cost-effective and environmentally friendly disposal.
Disposal of sludge
Under strict environmental regulations, disposing of such a large amount of sludge in a sustainable manner is a difficult undertaking. Sludge has been recognised for use as a raw material in the manufacture of cement, bricks, and artificial aggregates, as a cementitious material, and as a sand substitute in the preparation of concrete and mortar all over the world.
What is sewage sludge?
Sewage sludge contains both inorganic and organic materials, as well as high levels of some plant nutrients, as well as much lower levels of several trace elements and organic compounds, as well as pathogens. Depending on the wastewater composition and treatment procedures utilised, sewage sludges have a wide range of compositions.Because of mandated industrial pre-treatment of wastewater, the concentrations and incidence of trace metals and other contaminants in sewage sludge have dropped significantly during the last 20 years.
Some of the remaining trace elements and organic compounds come from human waste and consumer product disposal, but corrosion of plumbing systems and water mains accounts for a large part. Because stormwater drains in certain cities are connected to sanitary sewer systems, some contaminants from the street debris and rainwater are retained in the sewage sludge.
How do you Calculation of sludge generated in WWTP?
This formula will establish the daily sludge production of a wastewater treatment plant:
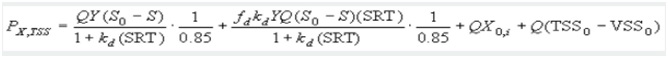
Where,
Q = influent flowrate[m3/d],
Y = biomass yield[g VSS/g COD used],
S0 = influent soluble substrate concentration (bsCOD)[g bsCOD/m3],
S = effluent soluble substrate concentration (bsCOD)[g bsCOD/m3],
kd = endogenous decay coefficient[g VSS/g VSS?d].
SRT = Sedimentation Retention Time[d],
fd = fraction of biomass that remains as cell debris[g VSS/g VSS],
Xo,i = nbVSS concentration in influent[g nbVSS/m3],
VSS0 = influent Volatile Suspended Solids[g VSS/m3] or [mg/l]
TSS0=influent Total Suspended Solids[g TSS/m3] or [mg/l]




