An overview of designing an ETP Plant for Paper Manufacturing
Effluent treatment is essential for industries to minimize environmental pollution and ensure the safe discharge of treated wastewater into natural water bodies.
The paper manufacturing industry generates significant amounts of effluent containing suspended solids, dissolved organic and inorganic substances, and high levels of biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD). An Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) is necessary to treat the effluent before discharge.
Now let us begin and discuss the design and working process of an ETP for a paper manufacturing unit.
Design.
The design of an ETP depends on various factors, including the type and amount of effluent generated, treatment objectives, discharge regulations, and available land. The following are the steps involved in the design of an ETP for a paper manufacturing unit:
1. Characterization of Effluent:
The first step is to analyze the effluent characteristics, such as pH, BOD, COD, suspended solids, and total dissolved solids. The paper industry effluent contains a high amount of suspended solids, BOD, and COD.
2. Treatment Objectives:
The next step is to determine the treatment objectives, such as the removal efficiency of BOD and COD, and the desired final effluent quality. The discharge limits for paper manufacturing units in India are as follows: pH 5.5-9.0, BOD <30 mg/L, COD <250 mg/L, and TSS <100 mg/L.
Process Flow Diagram of an ETP for a Paper Manufacturing Unit.
The following is the process flow diagram of an ETP for a paper manufacturing unit:
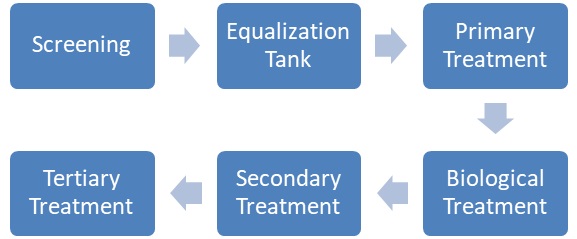
Selection of Treatment Technologies:
Based on the effluent characteristics and treatment objectives, various treatment technologies such as physical, chemical, and biological can be used. In the case of paper industry effluent, biological treatment is the most effective method for BOD and COD removal. We at Netsol Water provide the best technology at economical prices. The following are the treatment technologies that can be used for an ETP for a paper manufacturing unit:
a. Screening: The effluent is first screened to remove large solids such as wood chips, bark, and other debris. This step prevents clogging and damage to downstream equipment.
b. Equalization Tank: The effluent is then collected in an equalization tank, which is designed to provide a consistent flow rate and load to the treatment plant. The equalization tank helps to reduce shock loads and fluctuations in the effluent quality.
c. Primary Treatment: The effluent is then passed through a settling tank, where the suspended solids settle at the bottom of the tank. The settled solids are removed as sludge and sent for further treatment.
d. Biological Treatment: The settled effluent is then passed through an activated sludge process, where microorganisms break down the organic matter into harmless substances. The activated sludge process is designed to provide sufficient oxygen and nutrients to the microorganisms for their growth and metabolism.
e. Secondary Treatment: The effluent is then passed through a clarifier, where the remaining suspended solids settle, and the clear water is discharged. The clarifier helps to separate the solids from the water, and the settled solids are removed as sludge and sent for further treatment.
f. Tertiary Treatment: The final step is the tertiary treatment, where the effluent is subjected to advanced treatment methods such as disinfection, membrane filtration, or reverse osmosis to meet the desired effluent quality. The tertiary treatment helps to remove any remaining pollutants and contaminants from the effluent, ensuring that it meets the discharge standards.
Summary.
So the design of an effluent treatment plant for a paper manufacturing unit involves various steps, including the characterization of effluent, selection of treatment technologies, and determination of treatment objectives. The process flow diagram and working function of an ETP for a paper manufacturing unit have also been discussed in detail. The use of advanced treatment methods such as disinfection, membrane filtration, or reverse osmosis in the tertiary treatment stage can ensure that the effluent meets the desired quality standards before discharge. The design and operation of an efficient ETP can help minimize environmental pollution and ensure a safe discharge of treated wastewater into natural water bodies.
Leading manufacturer of sewage treatment plants in India.
Netsol Water is the leading manufacturer, supplier, and exporter of a quality selection of water treatment, and wastewater treatment products in India, by using advanced sewage treatment methods.
RO plants, water softeners, ETPs, STPs, DM plants, AMC, O&M, Ultra filtration, UV, Ozonation, ZLD plants, Anoxic tanks, and other goods and services are available from us. We also provide services to businesses in sectors including automotive, pharmaceutical, textile, pulp & paper, beverages, refineries, schools, hospitals, office buildings, and hotels, among others.
Call us at +91 9650608473 or email at enquiry@netsolwater.com for further information.



