- For Enquiry- 0120-2350053 || +91 9650608473 || +91 9650795306
- enquiry@netsolwater.com
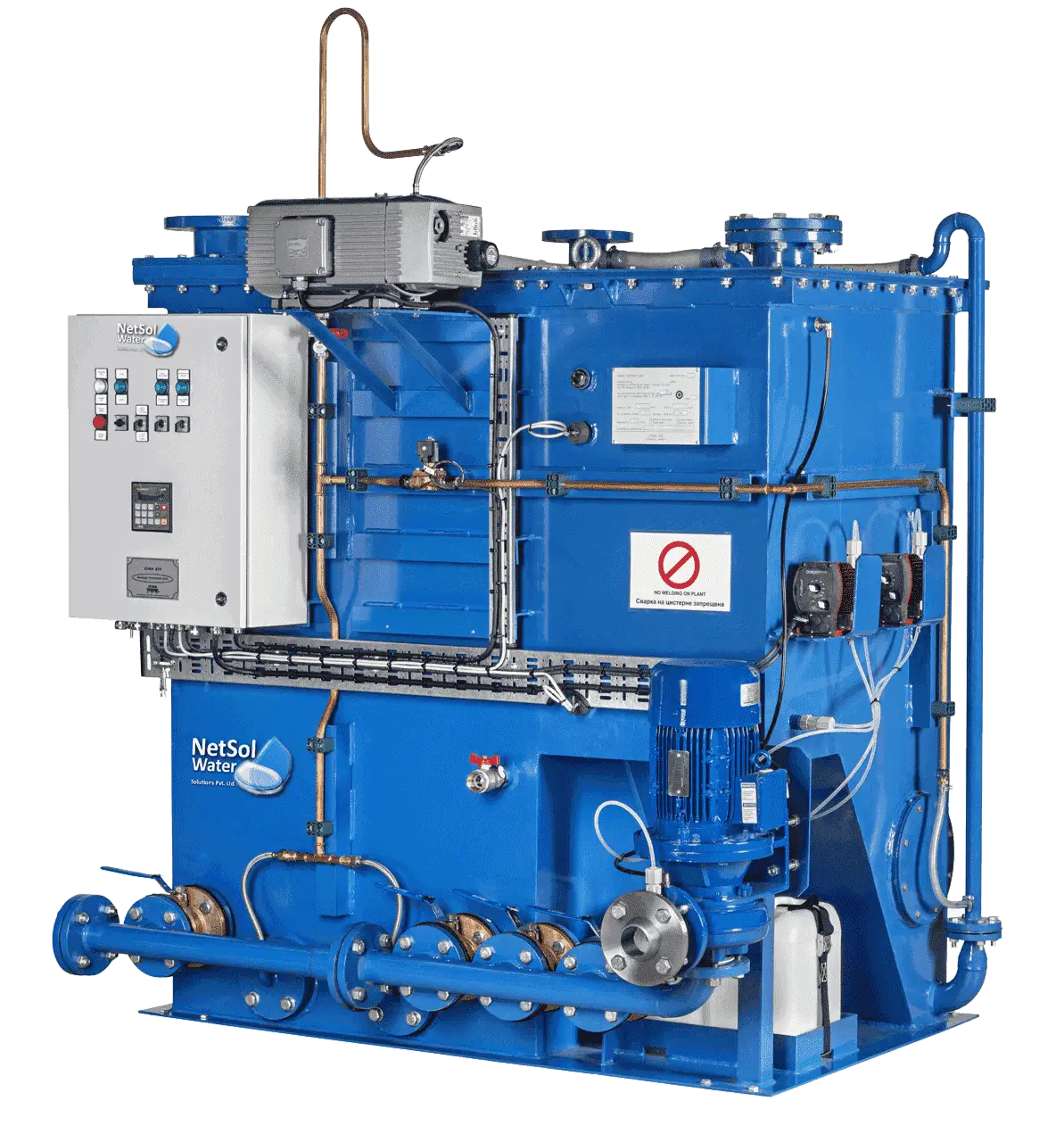



Sewage treatment Plant is that the process of removing contaminants from wastewater, primarily from household sewage. It includes physical, chemical, and biological processes to get rid of these contaminants and produce environmentally safe treated wastewater (or treated effluent). A by-product of sewage treatment is typically a semi-solid waste or slurry, called sewage sludge that has got to undergo further treatment before being suitable for disposal or land application.
Sewage Treatment Plant can also be mentioned as wastewater treatment, although the latter may be a broader term which may even be applied to purely industrial wastewater. Surface runoff and effluents from small-scale industries or pre-treated industrial wastewaters are sometimes routed through municipal sewage treatment plants when the environmental advantages of treatment outweigh the disadvantages of reduced treatment efficiency. Dilution of sewage by storm water runoff or industrial wastewater with low biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) decreases the efficiency of secondary treatment; because secondary treatment ecosystems require a minimum concentration of biologically decomposable waste to sustain the ecosystem population.
Effluent is usually discharged at a BOD concentration adequate to that required minimum, but it's going to be diluted to lower concentrations. In either case, the entire mass of BOD discharged to receiving waters is adequate to the discharge concentration times the flow volume; so dilution before secondary treatment reduces the waste concentration available to feed the ecosystem, and bigger volumes of dilute flow can discharge a greater mass of BOD. Industrial wastewater may contain pollutants which can't be removed by conventional sewage treatment; and variable flow of commercial waste related to production cycles may upset the population dynamics of secondary sewage treatment ecosystems. Sewage are often treated on the brink of where the sewage is made , which can be called a "decentralized" system or maybe an "on-site" system (in septic tanks, bio filters or aerobic treatment systems). Alternatively, it are often collected and transported by a network of pipes and pump stations to a municipal treatment plant. this is often called a "centralized" system, although the borders between decentralized and centralized are often variable.
Sewage is generated by residential, institutional, commercial and industrial establishments. It includes household waste liquid from toilets, baths, showers, kitchens, and sinks draining into sewers. In many areas, sewage also includes liquid waste from industry and commerce. The separation and draining of household waste into greywater and blackwater is becoming more common with in developed world, with greywater being permitted to be used for watering plants or recycled for flushing toilets.
Netsol water has extended its mechanical contracting offering its services thereby offering a single window approach to its customers for water wastage by using Sewage Treatment Plant.

